http://vitorr.com/post-details.php?postid=2615
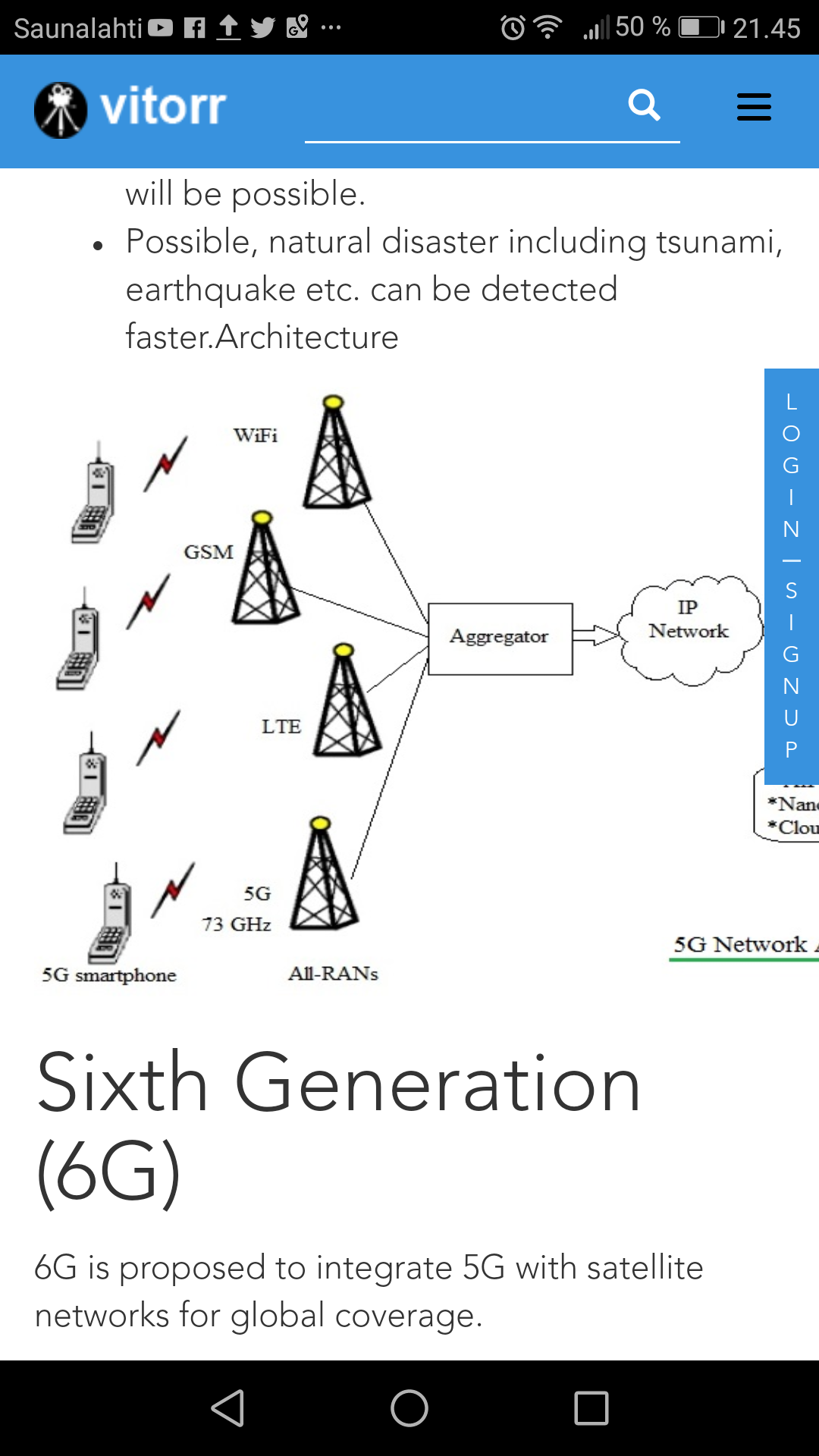
The cellular wireless Generation (G) generally refers to a change in the nature of the system, speed, technology and frequency. Each generation have some standards, capacities, techniques and new features which differentiate it from the previous one.
Now 5G is hot technology at the top of the hype cycle. But that’s not the end of story, because when we will see that 5G does not fullfill all the promises, we start looking for to implement next version after it: 6G.
316 Comments
Tomi Engdahl says:
Nokian Pekka Lundmark: Tämän takia 6G:tä tarvitaan
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14561-nokian-pekka-lundmark-taemaen-takia-6g-tae-tarvitaan
Nokian toimitusjohtaja Pekka Lundmark kertoi eilen Business Finland 6G-tapahtumassa omia näkemyksiään siitä, miksi tarvitsemme 6G-tekniikkaa. – Jos katsoo Netflixiä 5G:n yli, joku voi ajatella että tarvitsee nopeammin Netflixin. 6G ei ole vain lisää kapasiteettia, pienempää latenssia, parempaa luotettavuutta tai tietoturvaa.
- Se on toki kaikkia näitä, 10 kertaa nopeampi ja tuo alle millisekunnin latenssin, mutta minusta tärkeintä 6G:ssä on se, että se mullistaa verkkojen luonteen. 6G:n myötä verkot mahdollistavat sekä viestinnän että aistimisen (sensing) aivan uudella tavalla.
Mitä se sitten tarkoittaa, että verkko aistii? Lundmarkin mukaan kyse on aika yksinkertaisesta asiasta. Siitä, että objekteista takaisin kimpoavat signaalit mahdollistavat niiden muodon, sijainnin ja nopeuden määrittämisen.
- Nokia Bell Labsin tutkimuksessa olemme kehittäneet 6G-verkon, jolla voimme havaita liikkumien kohteiden muodon ja nopeuden. jos alkaa ajatella niitä sovellusmahdollisuuksia, mitä tämä avaa, se on aika häkellyttävää, Lundmark sanoi.
Tämän tekniikan vieminen laboratoriosta ihmisten arkeen muuttaa monia asioita. 6G tuo esimerkiksi älykaupungissa verkkoja, jotka voivat aistia ja ajatella tekoälyn avulla ja viestiä huippunopeasti alle millisekunnin viiveellä. – Jos vaikkapa lapsi erehtyisi menemään liikenteen sekaan, 6G-verkko voisi reagoida reaaliajassa ja estää onnettomuuden. 6G-pohjainen liikenteen valvontajärjestelmä voisi keskustella ajoneuvojen kanssa ja reagoida nopeammin kuin yksikään ihminen.
Tomi Engdahl says:
6G Bridgen tarkoitus pitää Suomi mobiilitekniikan kehityksen kärjessä
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14560-6g-bridgen-tarkoitus-pitaeae-suomi-mobiilitekniikan-kehityksen-kaerjessae
Business Finland julkisti eilen uuden 300 miljoonan euron ohjelman, jonka tavoite on pitää Suomi mobiilitekniikan kehityksen kärjessä. Business Finlandin pääjohtaja Nina Kopola muistutti, että tehtävä on vaikea. – Kilpailu kovenee koko ajan ja muut haastavat johtoasemaamme, Kopola sanoi.
6G Bridge jatkaa monen muun teknologiaohjelman työtä. Meillä panostettiin jo Tekesin aikaan uusien verkkosukupolvien kehitykseen. 5G-tekniikan kehitykseen perustettiin kahdeksan vuotta sitten 5thGear. Se oli viiden vuoden ja sadan miljoonan euron. hanke.
Eilen virallisesti startannut 6G Bridge kestää vuoden 2026 loppuun. Kopolan mukaan ohjelman tavoite on auttaa rakentamaan mobiileja ekosysteemejä ja myös houkuttelemaan investointeja Suomeen. Kopola muistuttikin, että innovaation merkitystä on mahdotonta yliarvioida.
- Miljoona päivää sitten aloimme tehdä työkaluja raudasta. 10 000 päivää sitten meillä ei ollut vielä mobiilia internetiä. Maailman pelastaminen on hyvää bisnestä, Kopola hehkutti.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Kiinnostaako 5G ja 6G? Nyt voit opiskella niitä ilmaiseksi
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14559-kiinnostaako-5g-ja-6g-nyt-voit-opiskella-niitae-ilmaiseksi
5G alkaa olla levinnyt useimpiin osiin Suomea ja nyt työ alkaa kohti 6G-verkkoja. Mutta mitä nämä pitävät sisällään? Siihen voi nyt jokainen paneutua Helsingin yliopiston avoimella verkkokurssilla. Kurssin lanseerasi tietotekniikan professori Sasu Sarkoma tänään Business Finlandin 6G-tapahtumassa.
Core 5G and Beyond
https://courses.mooc.fi/org/uh-cs/courses/5g-mooc
In this University of Helsinki open online course, you learn the fundamental concepts behind mobile networks, focusing in particular on 5G and the envisioned future 6G networks.
Tomi Engdahl says:
6G is Coming
Jan. 11, 2023
6G will have spectrum challenges, but its advantages will push wider adoption. Here are predictions for the technology in 2023 and beyond.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/analog/article/21257876/keysight-technologies-6g-is-coming?utm_source=EG+ED+Connected+Solutions&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230202043&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
What you’ll learn:
6G and its potential impact on upcoming events.
How 6G will be a perfect fit for the Gen-Z population.
Challenges with spectrum.
6G is on the horizon and its feature set will open new communication opportunities and address the continued demand for faster and more responsive wireless applications.
The new Olympic sport is the metaverse. The 2028 Summer Games will welcome 6G to the global stage. As a worldwide Olympic partner, expect Samsung to unveil a 6G deployment that will be a pivotal part of how viewers consume events. For example, you can expect one of the two Opening Ceremonies to happen in the metaverse.
Aggressive showcase objectives will become more visible, too. For example, the Japanese government plans to make the 2025 Osaka World Expo more visible as a 6G showcase.
The metaverse also will feature prominently in the user experience, enabling fans to participate in some Olympic events. In addition, we’ll see certain sports and, potentially, eSports run a 6G Metaverse Olympics in parallel with the actual Games, with at least one medal awarded within the metaverse. As brands draw inspiration from the Olympics, there will be a subsequent explosion of 6G use cases throughout 2028.
The arrival of 6G will open the door to new mobile network operators in the US. The tier one mobile network operators in the US have enjoyed a relatively stable market, but that is poised to change with the arrival of 6G. Similar to how Google Fiber enabled the company to enter into the ISP landscape, I think we’ll see Amazon, Microsoft, or another member of Big Tech capitalize on 6G to become a new tier one mobile network operator.
Ever used a Blackberry? Then 6G isn’t for you. 6G could be the sweet spot for Gen Z and the younger audience. The network is being built and set up for those currently 25 and under. These individuals are digital natives and they have no reservations about participating in virtual groups or sharing everything online. In 2023 and beyond, expect to see more discussion about how these younger generations will be monetized in 6G.
6G will foster a more geographically inclusive world, but it comes at a cost. Rural areas and remote industries like rail, offshore drilling, or broad mining will benefit from the enhanced connectivity of 6G. In addition, the network’s ultra-low latency will further accelerate high-speed finance. But these and other 6G benefits will come at a cost, as the technology will be far more expensive than its predecessors. Given this, you can expect adoption disparities.
Spectrum challenges will be a gatekeeper to further network innovation. 6G is coming and, while much work remains to actualize its potential, we have enough bandwidth to make it happen. Still, the industry is running short on spectrum, which will ultimately become a barrier to future technologies. As such, expect the 2030s to focus on solving the spectrum challenges to allow for future network innovations to thrive.
The current (misplaced) criticism about 5G not meeting expectations will begin to temper given the growing deployment of Rel-16 and early deployment of Rel-17 capabilities. These will enable the fuller realization of the original 5G vision.
The ITU will release the radio figures of merit for 6G as part of the ITU-R WP-5D 6G vision work. This will lay the groundwork for the targets that the industry must meet for the specifications to be worthy of IMT-2030
5G FR2/mmWave will grow, though slowly because the standard still requires more improvements in the standard, and the gradual reduction of cost of deployment.
What will not happen: No standards work will start on 6G. And it’s not likely they will start in 2024, either. This isn’t bad—6G is in research and there’s plenty of 5G standards work to be completed before the first study items for 6G begin.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Using Integrated Digital Twins to Continuously Assess the 6G Testbed
Feb. 1, 2023
This proposed testbed is intended for early and continuous assessment of relevant 6G technology elements on end-to-end user applications.
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/test-measurement/article/21259199/keysight-technologies-using-integrated-digital-twins-to-continuously-assess-the-6g-testbed?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Today&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230203075&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
What you’ll learn:
What will 6G bring to cellular networks?
How digital twins could help in the process of developing 6G standards.
Proposed idea of a 6G testbed with integrated digital twins.
Even as 5G cellular network deployments continue to ramp up within the U.S. and worldwide, major academic programs, research institutes, and commercial R&D operations are turning their focus toward deeper investigations into the promise and realization of 6G technology. Significant government investments have already occurred, and they’re expected to increase dramatically over the next few years. Nations are jockeying for a leadership position in 6G for both commercial and military use cases and seeding early explorations into technology and applications.1
The significant expansions anticipated in all of the usual metrics of cellular communication, including capacity, latency, device density, connection reliability, and other technology growth markers, is well documented.2 Also noteworthy is the burgeoning growth in the number and diversity of devices coming online via the rapidly expanding IoT.
Of course, to name a few areas of substantial growth, these will require significant technology breakthroughs in chipset design, antenna technology, ML-embedded networking, and real-time machine learning.
Tomi Engdahl says:
MWC23: Nokia kurottautuu pilveen – uusi logo lähes Kian tyyliin
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2023/02/26/nokialle-logo-lahes-kian-tyyliin-kurottautuu-pilveen/
Nokia julkisti tänään päivitetyn strategian, teknologiastrategian sekä uuden brändin Mobile World Congress 2023 -tapahtumassa Barcelonassa. Yhtiön logo muistuttaa tyyliltään paljolti korealaisen autonvalmistaja Kian aasialaista logotyyliä. Sillä mennään aina metaversiumiin asti.
Nokia esitteli Barcelonan mobiilimessuilla tähtäävänsä edelläkävijäksi tulevaisuuden pilviteknologiaan pohjautuvissa verkkoratkaisuissa aina metaversiumiin asti. Muutos on tulossa, sillä verkkojen merkitys kasvaa tulevaisuudessa, kun yritykset ympäri maailmaa panostavat digitalisaation hyödyntämiseen. ’
’Verkkojen todellisesta voimasta on nähty vasta häivähdys – tulevaisuuden kehittyneet, aistivat ja ajattelevat verkot eivät pelkästään yhdistä ihmisiä ja laitteita, vaan ne ovat mukautuvia, itsenäisiä ja helposti käytettäviä’’, sanoi Nokian toimitusjohtaja Pekka Lundmark Barcelonassa.
Nokia on saanut Lundmarkin mukaan jo ensimmäisen vaiheen eli teknologisen perustan kuntoon onnistuneesti päätökseen vuoden 2021 aikana. Vuonna 2022 yhtiö siirtyi strategian kiihdytysvaiheiseen ja aikoo jatkaa tämän eteenpäin viemistä sekä valmistautua skaalausvaiheeseen teknologiajohtajuuden ja kasvaneen asiakaskunnan vauhdittamina.
Päästäkseen uusiin tavoitteisiin Nokia keskittyy Lundmarkin mukaan erityisesti Nokia-brändin kehittämiseen, oikean osaamisen varmistamiseen, pitkän aikavälin tutkimus- ja kehitystyöhön erityisesti 6G:ssä sekä digitalisaation hyödyntämiseen omassa toiminnassaan. Siitä on saatu jo näyttöä kun yritys on saanut 5G-laitteiden piiri- ja teknologiakehityksen uuteen lentoon.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Satelliittiyhteys tulee älypuhelimiin – testausratkaisu valmis
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14644-satelliittiyhteys-tulee-aelypuhelimiin-testausratkaisu-valmis
Alun perin idea taisi olla Applen, että mobiiliverkkojen ulkopuolella esimerkiksi kolaritilanteessa älypuhelimen piti pystyä hälyttämään apua satelliittien välityksellä. Ideasta näyttää tulevan valtavirtaa, ja esimerkiksi Motorola esittelee Barcelonan kännykkämessuilla defy 2 -mallia, joka pystyy kaksisuuntaiseen viestintään satelliittien välityksellä.
Jokainen uusi toiminnallisuus edellyttää oman testausratkaisunsa. Mittaustalo Rohde 6 Schwarz esittelee Barcelonassa yhdessä moto defy 2:n valmistajan Bullittin kanssa tiettävästi ensimmäistä testauslaitteistoa, joka tukee uutta 3GPP Release 17 -standardissa määriteltyä satelliitti-mobiiliviestintää.
Rohde & Schwarzin testilaitteisto varmistaa, että SOS-viestit ja kaksisuuntaiset viestit toimivat luotettavasti eri skenaarioissa ei-maanpäällisten verkkojen (NTN, non-terrestrial networks) kautta 3GPP:n mukaisesti. MWC-messuilla Rohde & Schwarzin osastolla esitellään testikokoonpanoa, jossa on testtavana laitteena Bullittin 5G-älypuhelin, joka on varustettu MediaTekin piirisarjalla.
Tomi Engdahl says:
5G-tekniikka tuo tarkan laitepaikannuksen
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2023/02/24/5g-tekniikka-tuo-tarkan-laitepaikannuksen/
Nopeasti yleistyvät 5G-verkot mahdollistavat nopeamman tietoliikenneyhteyden lisäksi mahdollisuuden tarkkaan laitepaikannukseen satelliittipaikannuksen kannalta haastavissa ympäristöissä. Tampereen yliopistolla perjantaina 3.3. väittelevä DI Mike Koivisto on tutkinut tarkkaa paikannusta juuri 5G-verkkojen radiosignaaleja käyttäen.
Vaikka satelliittipohjainen paikannus on varteenotettava vaihtoehto avoimilla ulkoalueilla käytettäville paikkariippuvaisille sovelluksille, ei satelliittipohjainen paikannus ole optimaalinen vaihtoehto kaikkialla. Esimerkiksi suurten kaupunkien keskustoissa tai sisätiloissa satelliittien lähettämien radiosignaalien vääristymien tai estymisten takia.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Ouluun kaksi uutta 6G-piiriprofessuuria yritysrahoituksella
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2023/02/28/ouluun-kaksi-uutta-6g-piiriprofessuuria-yritysrahoituksella/
Oulun yliopisto lisää SoC-järjestelmäpiirien osaamista tulevaisuuden 6G-verkkojen osalta. Rahoituksen takana ovat Oulun kaupungin ja Nokian lisäksi piirivalmistajat Nordic Semi ja Mediatek.
Uudet viisivuotiset professuurit on suunnattu järjestelmäpiirien (System on Chip) suunnittelun tutkimiseen ja kehittämiseen. Professoreina ovat aloittaneet Lauri Koskinen piirit ja järjestelmät -tutkimusyksikköön ja Zaheer Khan, langattoman tekniikan Centre for Wireless Communications-keskukseen.
’’Siru- ja piiriteknologian järjestelmät mahdollistavat 5G:n laajaan käyttöön nyt ja tekevät saman myös 6G:ssä 2030-luvulla”
Yritykset rahoittivat kaksi tärkeää 6G-professuuria Ouluun
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14648-yritykset-rahoittivat-kaksi-taerkeaeae-6g-professuuria-ouluun
Nokian, Nordic Semiconductorin, MediaTekin ja Oulun kaupungin tuella on perustettu kaksi uutta järjestelmäpiiriteknologioiden professuuria Oulun yliopistoon. Järjestelmäpiiriteknologian professori Zaheer Khan (kuvassa) aloittaa langattoman tietoliikenteen CWC-keskuksessa. Lauri Koskinen on palkattu Piirit ja järjestelmät -tutkimusyksikköön (CAS, Circuits and Systems).
Professori Markku Juntti Oulun yliopiston langattoman tietoliikenteen keskuksesta hehkuttaa uusia professuureja. – Oulun ICT-ekosysteemi on ollut maailman johtavia langattoman teknologian luomisessa 3G-, 4G- ja 5G-verkkoihin. Nyt olemme edelläkävijä 6G:ssä, joka muuttaa maailmaa jälleen luultavasti jopa enemmän kuin aiemmat matkapuhelinsukupolvet ovat tehneet. Siru- ja piiriteknologian järjestelmät mahdollistavat 5G:n laajaan käyttöön nyt ja tekevät saman myös 6G:ssä 2030-luvulla, Juntti sanoo.
Uusista professoreista CWC:n Khan on tutkinut ennen kaikkea verkkojen adaptiivisuutta.
CAS-yksikössä aloittava Lauri Koskinen tunnetaan puolestaan sulautettujen laitteiden ja ohjainpiirien tehonkulutuksen kutistajana. Koskinen on yksi perustajista Minima Processorissa
Tomi Engdahl says:
Satelliittiyhteys onnistuu usein pelkällä ohjelmistopäivityksellä
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14647-satelliittiyhteys-onnistuu-usein-pelkaellae-ohjelmistopaeivityksellae
Barcelonan Mobile World Congressissa on nähty ensimmäistä kertaa laajemmin laitteita, jotka pystyvät hätätilanteessa ottamaan yhteyttä viranomaisiin satelliittiyhteyden välityksellä. 3GPP-terminologiassa kyse on NTN-linkistä. Useissa tapauksissa se edellyttää vain laiteohjelmiston päivittämistä.
Tällaista ”helppoa” NTN-ratkaisua IoT-laitteisiin esittelee MWC:ssä Murata, joka on toteuttanut ratkaisunsa yhdessä piilaaksolaisen NTN-operaattori Skylon kanssa. Skyo löytyy myös Bullittin messuilla julkaistun satelliittipuhelimen taustalta.
Skylon NTN-verkko on tuotu Muratan tyypin 1SC -moduuliin, joka on erittäin vähävirtainen IoT-piirisarja mobiiliverkkoihin. Moduuli on maailman pienin LTE Cat M/NB-IoT -moduuli, jolla on globaali sertifiointi ja NTN-toiminto. Se tukee GNSS-yhteyksiä ja eSINM-autentiointia.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Nokia and Bosch set a new bar for 5G positioning and look ahead to 6G #MWC23
https://www.nokia.com/about-us/news/releases/2023/02/21/nokia-and-bosch-set-a-new-bar-for-5g-positioning-and-look-ahead-to-6g-mwc23/
Nokia and Bosch set a new bar for 5G positioning and look ahead to 6G #MWC23
Proof-of-concept network in Germany demonstrated accuracy within 50 cm
Nokia and Bosch are continuing their joint research in 6G, exploring the integration of sensing technologies in future 6G systems
Espoo, Finland – Nokia and Bosch today announced that they have jointly developed 5G-based precision positioning technology intended for new Industry 4.0 use cases. The two have deployed the proof of concept in a Bosch production plant in Germany, where extensive tests under realistic manufacturing conditions have shown an accuracy within 50 cm in 90 percent of the factory footprint.
The positioning technology tracks mobile and portable devices connected to the 5G network, accurately determining their positions where no global navigation satellite service coverage is available, for instance in factories, warehouses or underground facilities. As part of the factory test, an enhanced private 5G network was able to determine the precise position of assets such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs), mobile robots and mobile control panels – tracking their movements throughout the plant in real time.
Traditionally, 5G positioning works by measuring the time it takes for mobile signals to travel from a mobile device to different base stations and anchor nodes in the network. As signals take longer to reach nodes that are further away, the positioning system can triangulate its source. Nokia and Bosch have built upon that foundation by equipping 5G nodes with multiple receive antennas, which enable the network to detect the incoming angles of signals. Advanced Nokia Bell Labs algorithms interpret this time-delay and angle-of-arrival information to determine the most probable position of the mobile device. Their proof-of-concept achieves a level of accuracy well beyond the current cellular position state-of-the-art, providing a sneak peek at what 5G networks, both public and private, will be capable of in the future.
Peter Vetter, President of Bell Labs Core Research at Nokia, said: “Bosch and Nokia Bell Labs foresee a future where networks do far more than communicate. Soon, 5G will track connected devices more precisely than satellites, in places satellites can’t reach. In the next decade, 6G will be capable of sensing all objects in their coverage areas regardless of whether they contain active radios. We are creating networks that will endow humans with a digital 6th sense.”
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2023/02/23/5g-ja-6g-verkkojen-perusteista-avoimet-nettikurssit/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=5g-ja-6g-verkkojen-perusteista-avoimet-nettikurssit
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.cnbc.com/2023/03/01/mobile-phone-inventor-next-generation-will-have-devices-in-their-skin.html#Echobox=1677654497-1
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.erillisverkot.fi/satelliitit-tulossa-5g-verkon-tueksi/
https://sat5g-project.eu/
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.erillisverkot.fi/satelliitit-ja-5g-kolme-kovaa-etua/
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://5gtieto.fi/blogi/satelliitit-tukiasemat/
Tomi Engdahl says:
Uusi NTN-tekniikka: 5G korvaa satelliittipuhelimet
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/13928-uusi-ntn-tekniikka-5g-korvaa-satelliittipuhelimet
Kesällä 3GPP-järjestössä hyväksytty uusi 5G-standardi eli Release 17 tuo monia uudistuksia ja laajennuksia 5G-verkkostandardeihin. Yksi uudistuksista on NTN (Non-terrestrial networks), joka laajentaa 5G-yhteydet avaruuteen. Mediatek on jo demonnut NTN-datansiirtoa yhdessä mittauslaitevalmistaja Rohde & Schwarzin kanssa.
Uuden 5G-standardin NTN-osa tuo mukaan uusia verkkotopologioita. Niiden avulla linkit toimivat sekä korkealla että matalalla radalle lentäviin satelliitteihin. Tarkoitus ei ole, että NTN kattaa vain puhelu- ja laajakaistapalvelut, vaan yhteyksien pitää tukea myös NB-IoT- ja LTE-M-tyypin IoT-linkkejä.
Suurimmat haasteet tekniikassa liittyvät satelliittien korkeuteen ja kovaan nopeuteen. Korkeus johtaa suuriin häviöihin signaalipolulla ja pidempään RTT-kiertoaikaan radiosta radioon. Matalan radan LEO-satelliiteissa radiolinkki kärsii suuresta Doppler-ilmiöstä ja lisäksi maa-asemat pitää vaihtua nopeasti.
Haasteita siis riittää NTN-tekniikan kehityksessä. Kehitys kuitenkin etenee kovaa vauhtia. Ericsson, Qualcomm ja Thales ilmoittivat pari viikkoa sitten kehittävänsä LEO-satelliittien kautta toimivia 5G-yhteyksiä.
Vieläkin pidemmällä kehityksessä on Mediatek, joka raportoi testanneensa NTN-yhteyksiä laboratoriossa ensimmäistä kertaa. Rohde & Achwarz toimitti kokeeseen kanavaemulaattorin, jolla päätelaite saatiin ”liittymään” 600 kilometrin korkeudessa ja 27 000 kilometriä tunnissa kulkevaan satelliittiin.
Päätelaite oli varustettu Mediatekin NR NTN -testipiirisarjalla. Taiwanissa sijaitsevaan ITRI-tutkimuskeskukseen oli rakennettu demossa tarvittava maa-asema.
Myös Nokia on kiinnostunut satelliittiyhteyksistä. Aiemmin tässä kuussa yhtiö ilmoitti, että AST SpaceMobile aikoo viedä Nokian AirScale-tukiasemia taivaalle, jolloin satelliittiyhteyksiä voisi käyttää tavallisilla puhelimilla.
Tomi Engdahl says:
23.11.2022 5G uutisia 6G:stä ja työstä sen edistämiseksi, satelliiteista, 5G:n hyödyntämisestä terveysteknologiassa ja operaattoreiden terveiset
https://www.traficom.fi/fi/23112022-5g-uutisia-6gsta-ja-tyosta-sen-edistamiseksi-satelliiteista-5gn-hyodyntamisesta
Marjo Uusi-Pantti: VTT:n mikroelektroniikan ja kvanttiteknologioiden johtaja Tauno Vähä-Heikkilä mitä VTT:llä tehdään tällä hetkellä satelliittien kanssa?
Tauno Vähä-Heikkilä: Satelliittien kanssa tehdään VTT:llä hyvinkin monenlaisia asioita. Viimeisimpinä ehkä, jos katsotaan kokonaisuuksista, on tämmöiset pienet satelliitit ja pieniin satelliitteihin liittyvä tutkimuskehitystoiminta, jossa suomalaiset ovat menneet aika etukenossa maailmalla liittyen sekä tietoliikennepuoleen, että toisaalta sitten uusiin sensoriteknologioihin.
Jos tietoliikenne puolta katsotaan, niin pienet satelliitit ja niistä tehtävät konstellaatiot eli tarkoittaa, että meillä on yhden satelliitin sijasta sata satelliittia matalilla kiertoradoilla ja niillä voidaan toimittaa tietoliikenneyhteydet. Esimerkiksi Ukrainassa nyt on nähty, miten pienet satelliitit ovat olleet hyvin tärkeässä roolissa, niillä on pystytty tuottamaan tietoliikenneyhteydet ukrainalaisille, vaikka maan tietoliikenneverkko on välillä kokonaan maan tasalla eli pois käytöstä.
Nyt olemme tehneet tietoliikennesatelliitin yhdessä Kuva Spacen kanssa, tai se oli Reaktor Space Lab silloin, joka on noin kahden-kolmen maitopurkin kokoinen, sillä voidaan tehdä erittäin nopeita tietoliikenneratkaisuja tulevaisuudessa tämän tyyppisillä satelliiteilla. Ja se mitä olemme nyt tehneet, niin on satelliitti, joka toimii noin 10 – 15 kertaisilla taajuuksilla, ehkä suuremmillakin verrattuna nykyisiin 5G tietoliikennejärjestelmiin ja matkapuhelimiin, eli satelliitti toimii 76 GHz:n taajuudella, mikä on ensimmäistä kertaa maailmassa, mitä tämän tyyppistä työtä on tehty ja toteutettu. Me pystymme ottamaan myös vastaan tätä signaalia VTT:lle Espooseen ja samassa projektissa ollaan Itävaltaan otettu tietoliikenneyhteys avaruudesta.
Suurin osa tämän hetkisestä tietoliikenteestä maapallolla tapahtuu maanpäällisillä verkoilla, mutta satelliiteista voi olla apua hyvinkin monessa eri tapauksessa. Esimerkiksi Ukrainassa on nyt ollut sodan aikana paljon apua tietoliikenteestä ja myös kuvantavista satelliiteista, jotka ovat tuoneet tilannekuvaa eli kuvia mitä tapahtuu missäkin. Jos mietitään siviilisovelluksia, ja 5G:tä, ja 5G:n evoluutiota tai 6G:tä, niin niissä tulee olemaan satelliittitietoliikenne osana näitä kokonaisjärjestelmiä.
Suomessa on erittäin hyvät matkapuhelinverkot eli välttämättä tiedonsiirtoon satelliitista matkapuhelimeen, ei välttämättä ole ensimmäinen sovelluskohde Suomessa. Mutta jos mennään vähän harvemmin asutuille alueille tai isompiin valtioihin, esimerkiksi Yhdysvallat tai Keski-Eurooppa tai Pohjois-Suomikin, niin siellä yksi haaste on, että ei voida rakentaa niin tiheitä matkapuhelinverkkoja, että olisi aina erittäin hyvät matkapuhelinyhteydet. Tällöin satelliiteilla voidaan tuoda paikallisesti esimerkiksi johonkin kylään, pieneen kaupunkiin satelliittitietoliikenneyhteys, jossa se jaetaan maan päällä normaalilla matkapuhelinverkolla.
Toinen tapaus mikä ehkä näkyy teollisuudessa, on esimerkiksi laivaliikenne, eli satelliiteilla pystytään tuomaan laivoihin, ja tuodaan nykyisinkin jo tietoliikenneyhteyksiä. Nähtävissä on, että näiden piensatelliittikonstellaatioiden avulla pystytään tuomaan suuremmat tietoliikennenopeudet ja pienemmät viiveet tiedonsiirtoon.
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14644-satelliittiyhteys-tulee-aelypuhelimiin-testausratkaisu-valmis
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/tekniset-artikkelit/13-news/14647-satelliittiyhteys-onnistuu-usein-pelkaellae-ohjelmistopaeivityksellae
Tomi Engdahl says:
Advanced 6G Research Focus of Joint Effort
March 29, 2023
The research program will develop novel techniques for channel sounding and communication channel sensing in new 6G frequency bands.
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/test-measurement/article/21262841/microwaves-rf-anritsu-and-aalborg-university-cooperate-to-advance-6g-research?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Today&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230331051&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Anritsu expanded its 6G activities with innovative research by joining forces with Aalborg University in Denmark. This 6G research program will develop novel techniques for channel sounding and communication channel sensing in the new 6G frequency bands, including the millimeter-wave and sub-terahertz bands. The team will use vector network analyzers from Anritsu that have specific features to empower measurement methods leveraging antenna and measurement systems technology from Aalborg University.
To optimize the frequencies and waveforms for next-generation mobile communications like 6G and IMT-2030, it’s critical to have a detailed understanding of radio channel characteristics. Enabling advanced techniques for high-resolution and wide-bandwidth radio channel characterization, the research program also will support the evaluation of “Joint Communications and Sensing” techniques and waveforms currently being researched.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Metadevices Tackle the Terahertz Gap
April 10, 2023
Metadevices are redefining how electromagnetic fields and energy can be manipulated, enabling creation of solid-state devices for the terahertz spectrum.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/communications/article/21263599/electronic-design-metadevices-tackle-the-terahertz-gap
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://techxplore.com/news/2023-04-photonic-filter-noise-future-6g.html
Tomi Engdahl says:
The 7 Pillars of 5G/6G RF System Design (Part 1)
April 18, 2023
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/software/article/21263778/ansys-the-7-pillars-of-5g6g-rf-system-design-part-1?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Today&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230414056&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Designers of 5G/6G systems must take into account the seven major “pillars” critical to their successful creation, which center around antennas, receivers, and RF power, among other key issues.
What you’ll learn:
The many technical factors that must be assessed in 5G antenna design, including their interactions.
Further physical/environmental considerations for both the antenna and the entire system.
We can logically extend the above to any endeavor in High Technology, and particularly to one of the leading sectors for innovation at the chip, system, and software level: RF communication systems in 5G/6G. At the heart of these communications systems lies the physical layer, involving modulation, transmission, and de-modulation of signal and data content over the wireless channel. Operating the physical layer reliably has implications on the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the equipment, which is the single overriding concern for the customer service provider (CSP) purchasing, operating, and maintaining that equipment.
What, then, are the pillars that serve as major considerations in 5G/6G physical-layer design?
1. RF power
2. Antenna sizing
3. Antenna agility and beamforming
4. RF bandwidth
5. RF waveform selection
6. Receiver design
7. Bespoke wireless channel modeling
What’s the Prognosis?
One can readily discern that these pillars are significantly more complex in terms of instantiation than for most problems because of their evident dynamic interactivity and interdependence. Furthermore, many advanced design options and their attendant issues are subject to significant repercussions from these primary design pillars.
Such repercussions include channel latencies, the “densification” of hierarchical networks (from femtocells and microcells up to base stations and the extension to air- and space-based non-terrestrial/satellite nodes), edge processing, the downstream impact on 6G, implications for optical backhaul and consequences to processing support (including asymmetric heterogeneous multiprocessing), to name a few.
With all this in mind, what is the path of wisdom a design team should follow for building the pillars for a house such as this? We will discuss them all in a series of articles that will give each topic justice. The next installment of this series will detail the first pillar described above: RF Power.
Tomi Engdahl says:
John D. McKinnon / Wall Street Journal:
The White House meets with corporate, government, and academic experts to begin developing strategies for 6G, as the US seeks to build an early lead over China
U.S. Begins Planning for 6G Wireless Communications
Biden administration aims to reassert U.S. leadership in telecom, an area where China has made gains
https://www.wsj.com/articles/u-s-begins-planning-for-6g-wireless-communications-246868d0?mod=djemalertNEWS
WASHINGTON—The Biden administration is beginning to plan for 6G wireless telecommunications, seeking to expand internet access while reasserting U.S. leadership in a sector where China has notched gains.
The White House on Friday will meet with corporate, government and academic experts to begin developing goals and strategies for the new 6G communications technology, which would have the ability to take cloud computing and the mobile internet to true global ubiquity, among other improvements.
The next generation of telecom is still years away from deployment, but it could pave the way for global internet access still unavailable with the current 5G standard, which makes smartphone downloads and wireless hot-spot connections faster. Expanding access to the internet has been a priority for the Biden administration as part of its infrastructure initiatives.
The 6G planning initiative also aims to reassert the leadership of the U.S. and its allies in telecommunications, where China has made gains thanks in part to careful nurturing of homegrown equipment manufacturing and increased participation in international standard-setting.
An administration official acknowledged that China used 5G effectively to advance its economic and national-security goals, such as gaining global market share over the West for its telecom-manufacturing companies, including Huawei Technologies Co.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Huawei kiihdyttää 5G:n vauhdin 10-kertaiseksi
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14873-huawei-kiihdyttaeae-5g-n-vauhdin-10-kertaiseksi
5G-yhteyksissä päästään tällä hetkellä noin gigabitin datanopeuksiin, kun verkko-olosuhteet ovat ihanteelliset. Huawei on tuomassa tarjolle 5.5G-tekniikkaa, jossa langaton nopeus olisi 10-kertainen. Siis 10 gigabittiä sekunnissa.
Analyytikoille Shenzhenissä järjestelmässään tapahtumassa Huawei kertoi lisätietoja Net5.5G-nimellä kulkevasta projektistaan, sekä niistä vaatimuksista, joita verkolle on asetettu. Esimerkiksi kotona 8K-tasoisen H.264-pakatun striimin siirto vaatii yli 3 gigabitin kaistanleveyttä.
Yrityksissä esimerkiksi holografinen interaktiivinen suunnittelu vaatii vähintään gigabitin yhteyttä alle 10 millisekunnin latenssilla. Jos halutaan valvoa sähköverkkoa tai tehtaan automaatiota reaaliaikaisesti, tarvitaan yli 10 gigabitin runkoverkkoa, alle 1 millisekunnin latenssia alle 20 mikrosekunnin värinää (jitter) esimerkiksi tuotantolinjan PLC-ohjauksessa.
Tämä 10 gigabitin yhteys vaatii käytännössä 800G-tasoisia runkoverkkoyhteyksiä. Vasta sen myötä pilvipalveluiden ja päätelaitteiden väliin saadaan riittävän nopea, reaaliaikaisuutta vastaava yhteys.
Tomi Engdahl says:
The 7 Pillars of 5G/6G RF System Design (Part 1)
April 12, 2023
Designers of 5G/6G systems must take into account the seven major “pillars” critical to their successful creation, which center around antennas, receivers, and RF power, among other key issues.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/eda/article/21263789/ansys-the-7-pillars-of-5g6g-rf-system-design-part-1?utm_source=EG+ED+Analog+%26+Power+Source&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230406061&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Tomi Engdahl says:
Advanced 6G Research Focus of Joint Effort
March 29, 2023
The research program will develop novel techniques for channel sounding and communication channel sensing in new 6G frequency bands.
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/test-measurement/article/21262841/microwaves-rf-anritsu-and-aalborg-university-cooperate-to-advance-6g-research?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Today&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230331051&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Tomi Engdahl says:
China Tests Ultra-fast Wireless Internet with 300Gbps Download Speed, Sparking 6G Rumors
https://www.gizmochina.com/2023/04/24/china-6g-300gbps-wireless-internet/
With 5G wireless communication technology already being implemented around the world, the focus has shifted to the next generation of wireless networks, 6G. While 5G is already a significant improvement over previous wireless technologies, 6G is expected to bring even more advancements in terms of speed, latency, spectrum, artificial intelligence, security, and energy efficiency. In this regard, understanding the possible differences between 5G and 6G is crucial to grasp the potential of the future of wireless communication. While 5G is still in the process of being rolled out globally, the research and development of 6G is already underway. As per latest reports, China has been testing ultra-fast wireless internet, with download speeds hitting 300Gbps.
US Concerned regarding China’s success with High-Speed Connectivity
The race for 6G is heating up, and the US is afraid of falling behind.
Tomi Engdahl says:
From 5G to 6G—Challenges, Technologies, and Applications
https://www.mdpi.com/1999-5903/14/4/117?utm_campaign=journnews_ccbj_futureinternet&utm_medium=social_journ&utm_source=facebook
As the deployment of 5G mobile radio networks gains momentum across the globe, the wireless research community is already planning the successor of 5G. In this paper, we highlight the shortcomings of 5G in meeting the needs of more data-intensive, low-latency, and ultra-high-reliability applications. We then discuss the salient characteristics of the 6G network following a hierarchical approach including the social, economic, and technological aspects. We also discuss some of the key technologies expected to support the move towards 6G. Finally, we quantify and summarize the research work related to beyond 5G and 6G networks through an extensive search of publications and research groups and present a possible timeline for 6G activities.
Keywords: 3GPP; 6G; artificial intelligence; beyond 5G; edge computing; next-gen; THz
Tomi Engdahl says:
Challenges In Packaging 5G And 6G
https://semiengineering.com/challenges-of-packaging-5g-and-6g/?cmid=1d01f162-3945-47ef-b029-1ef05607d230
From package-defined antennas to antenna-defined packages, and lots of tradeoffs in between.
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://hackaday.com/2023/05/25/a-mobile-phone-from-1985/
Tomi Engdahl says:
Nokia esittelee jo 6G-piirejä
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/15029-nokia-esittelee-jo-6g-piirejae
Yleisesti arvioidaan, että 6G-verkot voisivat tulla käyttöön joskus ensi vuosikymmenen vaihteessa. Alueen tutkimus etenee jo kovaa vauhtia, kuten Nokian Bell Labs -tutkimuskeskuksen ja mittaustalo Keysightin demot kansainvälisessä mikroaaltotekniikan symposiumissa kesäkuussa osoittavat.
Yritykset lupaavat esitellä San Diegon IMS 2023 -tapahtumassa tehovahvistinpiirin karakterisointia eli sen ominaisuuksia testaamista. Piirianalysaattori mittaa virhevektorin suuruutta Nokian tehovahvistimesta, joka on suunniteltu käytettäväksi tulevissa 6G-laitteissa. Testiä esitellään D- ja E-kaistoilla eli puhutaan yli 100 gigahertsin kaistanleveydestä.
Toisesa demossa esitellään E-kaistalla toimivaa radiotaajuista IC-piiriä. Se on suunniteltu tulevien verkkojen paluukanavalaitteiden lähetinvastaanottimia varten. Karakterisoinnin avulla Nokia Bell Labs ymmärtää paremmin komponenttien suorituskykyä, mikä mahdollistaa suunnittelun edelleen optimoinnin.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Suomi sopi 6G-yhteistyöstä korkealla tasolla
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2023/06/02/suomi-sopi-6g-yhteistyosta-korkealla-tasolla/
Suomi sopi tänään Yhdysvaltain kanssa 6G-vekkojen tutkimus- ja muustakin yhteistyöstä. Julkilausuman allekirjoittivat Suomessa vierailulla oleva Yhdysvaltain ulkoministeri Antony Blinken ja Suomen puolelta ulkoministeri Pekka Haavisto.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Nokia esittelee jo 6G-piirejä
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/15029-nokia-esittelee-jo-6g-piirejae
Yleisesti arvioidaan, että 6G-verkot voisivat tulla käyttöön joskus ensi vuosikymmenen vaihteessa. Alueen tutkimus etenee jo kovaa vauhtia, kuten Nokian Bell Labs -tutkimuskeskuksen ja mittaustalo Keysightin demot kansainvälisessä mikroaaltotekniikan symposiumissa kesäkuussa osoittavat.
Yritykset lupaavat esitellä San Diegon IMS 2023 -tapahtumassa tehovahvistinpiirin karakterisointia eli sen ominaisuuksia testaamista. Piirianalysaattori mittaa virhevektorin suuruutta Nokian tehovahvistimesta, joka on suunniteltu käytettäväksi tulevissa 6G-laitteissa. Testiä esitellään D- ja E-kaistoilla eli puhutaan yli 100 gigahertsin kaistanleveydestä.
Toisesa demossa esitellään E-kaistalla toimivaa radiotaajuista IC-piiriä. Se on suunniteltu tulevien verkkojen paluukanavalaitteiden lähetinvastaanottimia varten. Karakterisoinnin avulla Nokia Bell Labs ymmärtää paremmin komponenttien suorituskykyä, mikä mahdollistaa suunnittelun edelleen optimoinnin.
6G:lle kaavailtujen äärimmäisten tiedonsiirtonopeuksien, erittäin alhaisen latenssin ja lähes äärettömän kaistanleveyden tarjoaminen edellyttää nykyistä korkeammille taajuuksille menoa. Puhutaan alle terahertsin alueesta (sub-Terahertz) eli sadoista gigahertseistä. Niitä ei ole perinteisesti käytetty mobiiliviestintään, koska signaalien eteneminen (propagointi) aiheuttaa ongelmia eheyteen ja tuottaa polkuhäviöitä.
IMS 2023 -messujen demo perustuu Keysightin PNA-X Vector Component Analyzer -ratkaisuun
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2023/06/02/suomi-sopi-6g-yhteistyosta-korkealla-tasolla/
Tomi Engdahl says:
Oululaiset veivät uusimman 6G-lehtensä Göteborgiin
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2023/06/06/oululaiset-veivat-uusimman-6g-lehtensa-goteborgiin/
Oulun yliopiston julkaisema kuudes
Uusin 6G Waves nostaa esille suomalaisen alan viimeisimmän tutkimuksen nykytilan ja esittelee tutkimusaiheet sekä tietysti joukon ihmisiä 6G Flagshipin takana. Uusin numero keskittyy etenkin energia-alan ja terveydenhuollon teemoihin.
Teemat tulevat 6GESS-kokonaisuudesta (6G Enabling Sustainable Society), joka on neljän eri Oulun yliopiston tiedekunnan yhteistyötä. Siihen liittyy tekniikkaa, teknologiaa, lääketiedettä ja liiketoiminnan tutkimista. Numero käsittelee myös viimeisimpiä tutkimusuutisia ja avaa tulevaisuuden suunnitelmia. Se tarjoaa tietoa siitä, missä olemme teknologiakehityksessä nyt ja mitä voi tapahtua seuraavan kymmenen vuoden aikana alalla.
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/15068-110-gigahertsin-signaalia-mikroaalloille
Tomi Engdahl says:
R&S Hosts RF Design Challenge; Demos Sub-THz/6G Front End
June 2, 2023
Are you an RF genius? Find out at Rohde & Schwarz’s IMS 2023 booth and catch demos of numerous test products.
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/test-measurement/article/21267076/microwaves-rf-rs-hosts-rf-design-challenge-demos-subthz6g-front-end?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Show+Daily+Expo+News&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230609147&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
At IMS 2023 Booth 735, Rohde & Schwarz will showcase multiple live demos of cutting-edge test and measurement developments. IMS attendees can also participate in the interactive “Are you a genius?” RF Design challenge, putting their knowledge to the test through a series of lab challenges that evaluate an attendee’s knowledge of S-parameters, EVM, high power, and baseband measurements.
In addition to the RF Design Challenge, Rohde & Schwarz will highlight multiple demonstrations at the company’s booth. These include the new 67-GHz noise-figure measurement capability that further enhances the R&S ZNA vector network analyzer for full characterization of amplifiers and converters.
On the road to 6G, revolutionary technologies demand new ways of testing for the next generation of wireless communication. Several highlights at the Rohde & Schwarz booth are the latest solutions for early sub-terahertz and 6G research applications. The R&S FE170ST external front ends (see image above) extend the frequency ranges not only of the company’s signal and spectrum analyzers, but also of its signal generators up to the D-band (110 to 170 GHz), enabling engineers to access the range they need to develop the next generation of mobile communications. In addition, demonstrations of both the R&S ZNA vector network analyzers and the R&S FSWP phase-noise analyzer will highlight 6G D-band system and component characterization.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Keysight, Nokia Bell Labs Demo 6G Sub-THz Component Characterization
June 2, 2023
Keysight’s vector component analyzer and mmWave signal analyzer enable Nokia Bell Labs to better characterize component performance for 6G D-band comms and E-band backhaul systems.
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/test-measurement/article/21267095/microwaves-rf-keysight-nokia-bell-labs-demo-6g-subthz-component-characterization?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Today&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230609113&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
This article is part of our IMS 2023 coverage.
Visitors to Keysight Technologies’ Booth 835 at IMS 2023 can see the company’s demos (with Nokia Bell Labs) of component and RFIC characterization for 6G sub-THz RF applications in the D- and E-bands.
For 6G technology to deliver on its promised extreme data speeds, ultra-low latency, and near-infinite bandwidth, sub-THz spectrum will have to come into play. But sub-THZ frequencies haven’t traditionally been used for cellular communications due to their propagation characteristics, which present signal-integrity and path-loss challenges that can negatively impact performance.
To help mitigate those challenges, Keysight and Nokia Bell Labs have been collaborating to develop characterization techniques to test active sub-THz components, such as amplifiers, mixers, and frequency converters. The goal is to ensure that the components don’t introduce additional signal distortion into communications systems.
At IMS, the collaborators’ demo, built on Keysight’s PNA-X vector component analyzer, involves characterization of a Nokia power amplifier (PA) developed for use in 6G D-band wireless communications systems and designed to operate with a low error-vector magnitude (EVM).
Tomi Engdahl says:
Finallly, to help network equipment manufacturers, semiconductor companies, and device makers address the bandwidth and performance demands of 6G, Keysight will display a 6G sub-THz R&D testbed. The wideband testbed features an arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) that generates a wideband intermediate frequency (IF), which is upconverted to H-band (220-330 GHz).
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/test-measurement/article/21267095/microwaves-rf-keysight-nokia-bell-labs-demo-6g-subthz-component-characterization?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Today&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230609113&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Tomi Engdahl says:
Pickering to Showcase MEMS-Based PXI/PXIe Multiplexers
June 7, 2023
The new multiplexers are said to provide longer operational life, faster speeds, and higher bandwidths than electromagnetic relay alternatives.
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/test-measurement/article/21267369/microwaves-rf-pickering-to-showcase-memsbased-pxipxie-multiplexers?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Show+Daily+Expo+News&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230612192&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Tomi Engdahl says:
Active Diplexer and E-band Amplifier Enhance Long-Range Communications
June 1, 2023
Filtronic’s second-generation active diplexer follows the first-generation launch at IMS 2022.
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/embedded/systems/article/21267069/microwaves-rf-active-diplexer-and-eband-amplifier-enhance-longrange-communications?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Show+Daily+Expo+News&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230612192&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Tomi Engdahl says:
Software-Defined Front End Empowers Next-Gen Wireless Solutions
June 20, 2023
Developed by Analog Devices, the mixed-signal platform brings flexibility and speed to intelligent-edge design while simplifying electronic test.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/communications/article/21268159/microwaves-rf-softwaredefined-front-end-empowers-nextgen-wireless-solutions?utm_source=EG+ED+Analog+%26+Power+Source&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230615021&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
What you’ll learn:
The need for wider bandwidths and more rapid processing and analysis of data in wireless systems.
What does Apollo MxFE mixed-signal front-end platform bring to the table?
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/15201-tiesitkoe-taetae-ensimmaeinen-matkapuhelin-kehitettiin-neuvostoliitossa
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.tme.eu/fi/news/events/page/54071/leonid-kupriyanovich-puhelin-jota-kukaan-ei-tarvinnut/
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/embedded/software/article/21270823/ansys-the-7-pillars-of-5g6g-rf-system-design-part-2-rf-power?utm_source=RF+MWRF+Wireless+for+Consumers&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230804064&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Tomi Engdahl says:
Nokia esittelee jo 6G-piirejä
https://etn.fi/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=15029&via=n&datum=2023-05-31_15:26:03&mottagare=30929
Yleisesti arvioidaan, että 6G-verkot voisivat tulla käyttöön joskus ensi vuosikymmenen vaihteessa. Alueen tutkimus etenee jo kovaa vauhtia, kuten Nokian Bell Labs -tutkimuskeskuksen ja mittaustalo Keysightin demot kansainvälisessä mikroaaltotekniikan symposiumissa kesäkuussa osoittavat.
Yritykset lupaavat esitellä San Diegon IMS 2023 -tapahtumassa tehovahvistinpiirin karakterisointia eli sen ominaisuuksia testaamista. Piirianalysaattori mittaa virhevektorin suuruutta Nokian tehovahvistimesta, joka on suunniteltu käytettäväksi tulevissa 6G-laitteissa. Testiä esitellään D- ja E-kaistoilla eli puhutaan yli 100 gigahertsin kaistanleveydestä.
Toisesa demossa esitellään E-kaistalla toimivaa radiotaajuista IC-piiriä. Se on suunniteltu tulevien verkkojen paluukanavalaitteiden lähetinvastaanottimia varten. Karakterisoinnin avulla Nokia Bell Labs ymmärtää paremmin komponenttien suorituskykyä, mikä mahdollistaa suunnittelun edelleen optimoinnin.
6G:lle kaavailtujen äärimmäisten tiedonsiirtonopeuksien, erittäin alhaisen latenssin ja lähes äärettömän kaistanleveyden tarjoaminen edellyttää nykyistä korkeammille taajuuksille menoa. Puhutaan alle terahertsin alueesta (sub-Terahertz) eli sadoista gigahertseistä. Niitä ei ole perinteisesti käytetty mobiiliviestintään, koska signaalien eteneminen (propagointi) aiheuttaa ongelmia eheyteen ja tuottaa polkuhäviöitä.
Näitä onglemia ratkaistakseen Keysight ja Nokia Bell Labs ovat tehneet yhteistyötä kehittääkseen karakterisointitekniikoita aktiivisten korkeataajuuksisten komponenttien, kuten vahvistimien, sekoittimien ja taajuuden muuntimien testaamiseksi.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Sixth-Generation Networks Must Get Creative to Meet Future Demands
July 27, 2023
The complexity of 6G networks, which will be a boon to industrial and healthcare spaces, among others, will require innovative approaches to develop compatible systems, especially in terms of AI and ML.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/communications/article/21270386/benchmark-sixthgeneration-networks-must-get-creative-to-meet-future-demands?utm_source=EG+ED+Connected+Solutions&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230810132&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
What you’ll learn:
Further incorporation of AI/ML technologies into 5G and upcoming 6G systems.
The need to develop lower-cost products for the FR2 mmWave range.
6G’s role in the IIoT and healthcare.
How Benchmark can help in 6G system development.
In search of effective spectrum use, cellular wireless technology has advanced to today’s fifth-generation (5G) networks. But demands for more bandwidth and faster data transfers compel sixth-generation (6G) networks to be even more creative and efficient in their spectrum consumption than preceding generations.
To serve more users in terms of both people and connected devices, 6G networks will benefit from more mature enabling technologies, many of which were developed for its predecessors.
Currently, there’s no universally accepted definition of what qualifies as 6G technology. Yet, because of the infrastructure’s greater complexity and expanded reach (on the ground and in space as satellites become an integral part of the network), building 6G networks will take time and require greater attention to detail.
The 7 Pillars of 5G/6G RF System Design (Part 1)
April 12, 2023
Designers of 5G/6G systems must take into account the seven major “pillars” critical to their successful creation, which center around antennas, receivers, and RF power, among other key
https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/eda/article/21263789/ansys-the-7-pillars-of-5g6g-rf-system-design-part-1
Tomi Engdahl says:
Sixth-Generation Networks Push New Boundaries
Aug. 2, 2023
The complexity of 6G networks, which will be a boon to industrial and healthcare spaces, among others, will require innovative approaches to develop compatible systems, especially in terms of AI and ML.
Hank Ly
https://www.mwrf.com/technologies/components/article/21270393/benchmark-sixthgeneration-networks-push-new-boundaries