http://vitorr.com/post-details.php?postid=2615
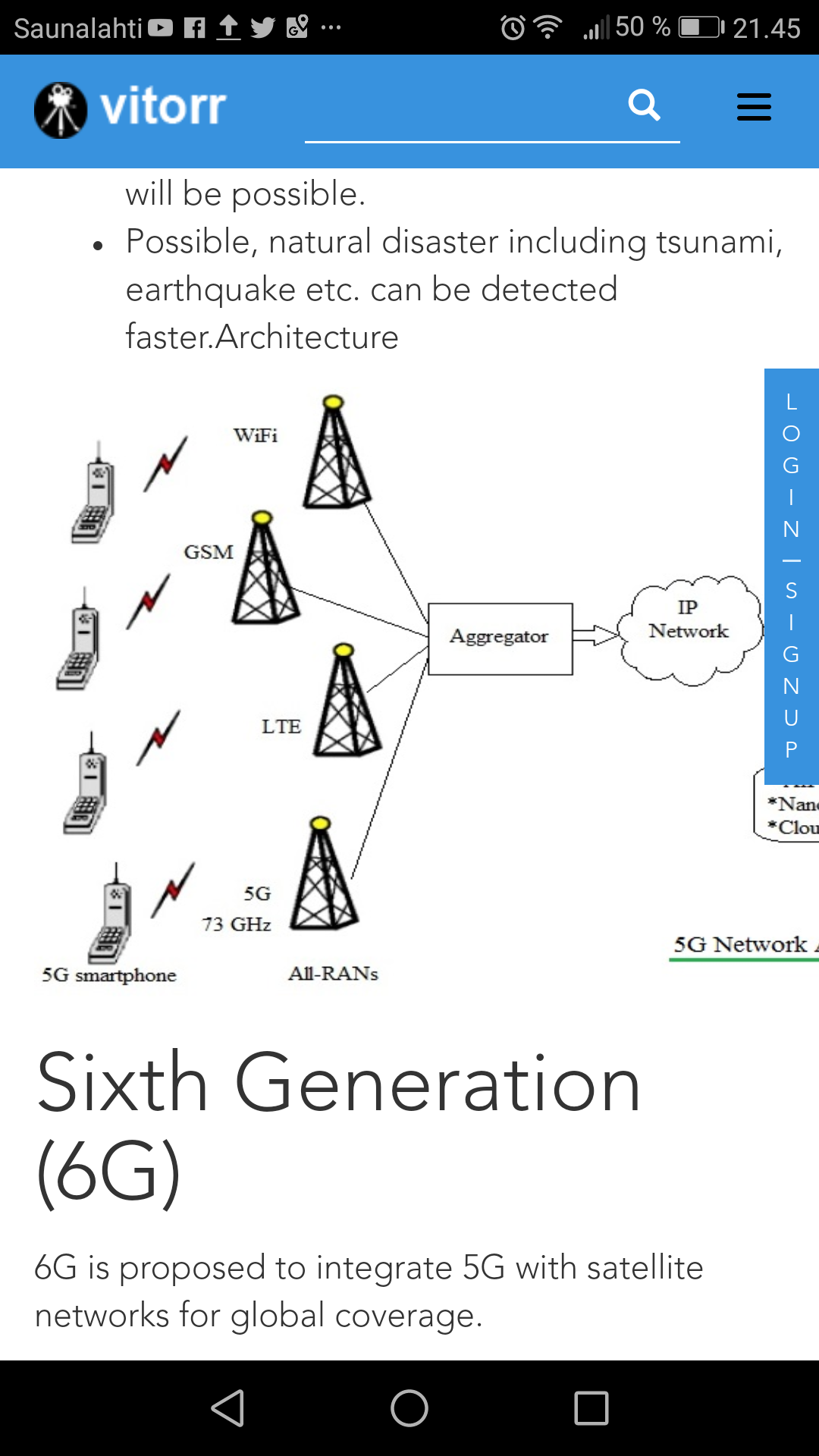
The cellular wireless Generation (G) generally refers to a change in the nature of the system, speed, technology and frequency. Each generation have some standards, capacities, techniques and new features which differentiate it from the previous one.
Now 5G is hot technology at the top of the hype cycle. But that’s not the end of story, because when we will see that 5G does not fullfill all the promises, we start looking for to implement next version after it: 6G.
533 Comments
Tomi Engdahl says:
5G-satelliittiyhteydet ovat siirtymässä tutkimus- ja pilottivaiheesta kohti kaupallista todellisuutta. Anritsun 5G RF -testausjärjestelmä on saanut maailman ensimmäisen PTCRB-hyväksynnän 5G NR NTN -testitapauksille, mikä avaa virallisen sertifiointipolun satelliitteihin kytkeytyville 5G-päätelaitteille.
NTN (Non-Terrestrial Network) tarkoittaa 5G-verkkoa, jossa maanpäällistä infrastruktuuria täydennetään matalalla, keski- ja geostationaarisella kiertoradalla toimivilla satelliiteilla. 3GPP:n Release 17 -määrittely toi NR NTN:n osaksi 5G-standardia, jolloin päätelaitteet voivat käyttää samaa 5G-protokollaa sekä tukiasemiin että satelliitteihin yhdistettäessä.
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18346-5g-satelliittilaitteiden-sertifiointi-voi-nyt-alkaa
Tomi Engdahl says:
Satelliiteista tulee olennainen osa 6G-verkkoja
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18330-satelliiteista-tulee-olennainen-osa-6g-verkkoja
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18311-nordic-laajentaa-iot-yhteydet-maanpinnalta-satelliitteihin
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18302-kevyempi-5g-on-sopiva-useimpiin-autoihin
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18318-haeiritsivaetkoe-muskin-satelliitit-tietoliikennettae-tahallaan
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2025/12/09/uusinta-6g-tietoa-tarjolla-lehdesta-ja-laboratoriosta/
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2026/01/08/vtt-ja-anritsu-testasivat-d-kaistan-huippunopeaa-tiedonsiirtoa/
Tomi Engdahl says:
Wi-Fi advocates get win from FCC with vote to allow higher-power devices
FCC says new category of devices “can operate outdoors and at higher power.”
https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2026/01/fcc-to-authorize-more-powerful-wireless-devices-in-6-ghz-wi-fi-band/
Tomi Engdahl says:
EU:n uusi verkkoasetus pakottaa operaattorit investoimaan
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18433-eu-n-uusi-verkkoasetus-pakottaa-operaattorit-investoimaan
Euroopan komission mukaan EU tarvitsee nopeammin valokuitua, kehittyneempiä mobiiliverkkoja ja turvallisia satelliittiyhteyksiä. Komission teknologiasuvereniteetista vastaava varapuheenjohtaja Henna Virkkunen korostaa, että suorituskykyinen ja häiriönkestävä digitaalinen infrastruktuuri on Euroopan kilpailukyvyn ja digitaalisen omavaraisuuden perusta.
Tätä tavoitetta tukemaan komissio esittää uutta Digital Networks Act -verkkoasetusta, joka uudistaa EU:n tietoliikenneverkkojen sääntelyä perusteellisesti. Asetuksen keskeinen vaikutus on se, että operaattoreita ohjataan ja osin myös pakotetaan investoimaan uusiin korkean kapasiteetin verkkoihin.
Komission mukaan nykyinen sääntely ei enää vastaa teknologian kehitystä eikä EU:n globaaleja kilpailutavoitteita. Uudistuksen ytimessä on aidosti yhtenäinen sisämarkkina verkoille.
Uuden asetuksen myötä operaattori tai palveluntarjoaja voisi tarjota palveluja koko EU:ssa rekisteröitymällä vain yhteen jäsenmaahan. Tämä vähentää hallinnollista taakkaa ja helpottaa rajat ylittävää toimintaa. Käytännössä muutos suosii EU-laajuisia toimijoita ja kiristää kilpailua kansallisilla markkinoilla. Kansallista sääntelyä yhdenmukaistetaan, vaikka viranomaisvalvonta säilyy jäsenmaissa.
Asetus muuttaa radiotaajuuksien käyttöä investointiystävällisemmäksi. Taajuusluvat pitenevät ja niistä tulee oletusarvoisesti uusittavia. Taajuuksien jakamista operaattoreiden kesken helpotetaan.
Satelliittiviestinnässä siirrytään EU-tason lupamalliin. Tämä mahdollistaa pan-eurooppalaisten satelliittipalvelujen rakentamisen ilman 27 erillistä lupaprosessia.
Merkittävin yksittäinen muutos koskee vanhoja kupariverkkoja. Digital Networks Act velvoittaa jäsenmaat laatimaan kansallisen siirtymäsuunnitelman, jossa kupariverkot ajetaan alas vuosina 2030–2035.
Suunnitelmat on toimitettava komissiolle vuonna 2029. Kuluttajille on samalla taattava selkeä tiedotus, palvelujen jatkuvuus ja toimivat korvaavat yhteydet. Käytännössä tämä tekee valokuidusta ja muista korkean kapasiteetin verkoista EU:n uuden perusinfrastruktuurin.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Iridiumin satelliitit keskustelevat kännyköiden kanssa softapäivityksen jälkeen
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18435-iridiumin-satelliitit-keskustelevat-kaennykoeiden-kanssa-softapaeivityksen-jaelkeen
Iridium Communications on ottanut merkittävän askeleen kohti suoraa satelliittiyhteyttä päätelaitteisiin. Yhtiö kertoo testanneensa onnistuneesti NTN-yhteyksiä, joissa viestit kulkevat suoraan matkapuhelin- ja IoT-laitteiden sekä Iridiumin LEO-satelliittien välillä. Kyse ei ole enää konseptista, vaan toimivasta yhteydestä oikeassa verkossa.
Testit tehtiin niin sanotusti on-air. Viestit välitettiin kaksisuuntaisesti Iridiumin olemassa olevan satelliittikonstellaation kautta. Yhteys perustuu 3GPP:n määrittelemään NB-IoT NTN -standardiin. Tämä on keskeistä, sillä ratkaisu ei vaadi omia, suljettuja teknologioita.
Oleellinen yksityiskohta on se, että NTN-toiminnallisuus aktivoitiin satelliitteihin ohjelmistopäivityksellä. Iridium hyödynsi ohjelmistoradioihin perustuvaa arkkitehtuuriaan. Uutta laitteistoa avaruuteen ei tarvittu.
Testeissä käytettiin Nordic Semiconductorin vähävirtaista nRF9151-piiriä. Kyse on tavallisesta LTE-M- ja NB-IoT-moduulista, joka tukee myös NTN-yhteyksiä. Tämä osoittaa, että satelliittiyhteys voidaan toteuttaa vakioiduilla, akulla toimivilla päätelaitteilla.
Iridiumin mukaan palvelu on suunnattu erityisesti operaattoreille. Sen avulla mobiiliverkkojen katvealueet voidaan paikata ilman uutta maanpäällistä infrastruktuuria. Samalla avautuu uusia käyttökohteita, kuten hätäviestintä, seuranta, logistiikka, maatalous ja kriittinen infrastruktuuri.
Yhtiö valmistelee parhaillaan testien beeta-vaihetta. Tavoitteena on kaupallinen NTN Direct -palvelu vuoden 2026 aikana. Jos aikataulu pitää, Iridiumista tulee ensimmäinen toimija, joka tarjoaa aidosti globaalin ja standardipohjaisen suoran satelliittiyhteyden päätelaitteille.
Tomi Engdahl says:
5G-verkon paikannus tarkentuu merkittävästi, sisälläkin alle metriin
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18439-5g-verkon-paikannus-tarkentaa-merkittaevaesti-sisaellaekin-alle-metriin
Ericsson tuo 5G Advanced -verkoihin merkittävän parannuksen paikannustarkkuuteen. Yhtiön mukaan 5G SA -verkkoon integroidulla ratkaisulla käyttäjän tai laitteen sijainti voidaan määrittää ulkotiloissa alle kymmenen senttimetrin tarkkuudella ja sisätiloissa alle metrin tarkkuudella. Kyse on selvästä harppauksesta aiempiin mobiilipohjaisiin paikannusmenetelmiin verrattuna.
Oleellista on, että paikannus on toteutettu suoraan 5G-verkon ydinominaisuutena. Operaattorin ei tarvitse rakentaa erillistä paikannusinfrastruktuuria, eikä päätelaitteisiin vaadita lisäantureita, sovelluksia tai beacon-verkkoja. Käytännössä palvelu voidaan ottaa käyttöön ohjelmistopäivityksellä 5G SA -verkossa.
Ulkotilojen senttitason tarkkuus perustuu Real-Time Kinematics -tekniikkaan, joka on tuttu tarkasta satelliittipaikannuksesta. Nyt vastaava tarkkuus tuodaan mobiiliverkkoon, jolloin paikannus toimii myös ympäristöissä, joissa GNSS-yhteydet ovat epäluotettavia. Sisätiloissa tarkkuus jää luonnollisesti heikommaksi, mutta alle metrin taso riittää jo moniin teollisiin ja turvallisuuskriittisiin käyttötapauksiin.
Ericsson korostaa myös sitä, että sama 5G-pohjainen paikannustekniikka toimii sekä sisällä että ulkona.
Energiatehokkuus on toinen keskeinen etu. 5G-verkon kautta tapahtuva paikannus kuluttaa vähemmän virtaa kuin satelliittipohjaiset ratkaisut, mikä on tärkeää erityisesti IoT-laitteissa, ajoneuvoissa ja drooneissa.
Operaattoreille Ericsson tarjoaa valmiit rajapinnat, joiden kautta sijaintitietoa voidaan hyödyntää suoraan sovelluksissa. Mahdollisia käyttökohteita ovat muun muassa virtuaaliset turva-alueet, omaisuuden ja ajoneuvojen seuranta, tuotannon ohjaus sekä henkilö- ja tavaravirtojen analysointi.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Voiko IoT edistää kestävää kehitystä?
https://etn.fi/index.php/tekniset-artikkelit/18440-voiko-iot-edistaeae-kestaevaeae-kehitystae
Internet of Things (IoT) nähdään usein energiasyöppönä ja elektroniikkajätettä lisäävänä teknologiana. Oikein suunniteltuna ja pitkä elinkaari huomioiden IoT voi kuitenkin muodostua keskeiseksi työkaluksi kestävän kehityksen edistämisessä – aina energiankulutuksen optimoinnista paristottomiin anturiratkaisuihin.
Kestävä tuotantotekniikka on tärkeässä asemassa, kun halutaan käyttää järkevästi planeetan äärellisiä luonnonvaroja. Vaikka termiä on käytetty viime vuosina mantran tavoin, siitä on myös muodostunut liiketoiminnan ja taloudellisen aktiviteetin keskeinen tukipilari.
Monissa kestävän tekniikan aloitteissa IoT toimii pääasiallisena laite- ja ohjelmistoalustana. Vaikka toteutukset vaativat alkuvaiheessa merkittäviä energiakustannuksia, pitkällä aikavälillä panostukset maksavat nopeasti itsensä takaisin.
Transforma Insightsin ja 6GWorldin raportin Sustainability in New and Emerging Technologies in 2023 mukaan IoT-tekniikan hyödyntäminen kattaa valmistamisen ja käyttöönoton vaatimat energiakustannukset. Sen lisäksi se tuo säästöjä noin kahdeksan kertaa enemmän kuin mitä energiakustannuksiin on kulutettu.
Keräämänsä datan ansiosta IoT hyvittää ympäristöjalanjälkensä jopa moninkertaisesti. Kun IoT:hen yhdistetään tehokkaasti esimerkiksi koneoppimisen sovelluksia, voidaan koota suuria tietomääriä. Näiden avulla ihmiset ja organisaatiot voivat ymmärtää paremmin omaa energiankulutustaan ja tehdä valveutuneita ympäristöön liittyviä päätöksiä. Päätöksentekoa voidaan myös automatisoida esimerkiksi älykkään energianjakelun avulla.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Älypuhelimen radio voi kutistua yhdelle sirulle
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18446-aelypuhelimen-radio-voi-kutistua-yhdelle-sirulle
Älypuhelimien radiot eivät ole vieläkään aidosti yhden sirun ratkaisuja. Vaikka modeemi ja signaalinkäsittely on jo pitkälti integroitu, RF-ketjun kriittiset suodattimet ovat yhä erillisiä komponentteja. Uusi tutkimus viittaa siihen, että tämä viimeinenkin este voidaan murtaa.
Tutkijat ovat kehittäneet pinta-akustisiin aaltoihin perustuvan akustisen laserin, joka tuottaa SAW-värähtelyt suoraan sirulla. Tähän asti SAW-suodattimet ovat vaatineet erillisiä pietsosähköisiä kiteitä ja ajureita. Juuri tämä on estänyt radion täyden integraation yhdelle piirille.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Ericsson ei usko RAN-markkinan kasvuun
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18445-ericsson-ei-usko-ran-markkinan-kasvuun
Ericsson ei odota radioverkkoliiketoiminnan (RAN) kasvavan vuonna 2026. Yhtiön mukaan markkina pysyy käytännössä paikallaan, ja kasvu haetaan muilta alueilta. Painopiste siirtyy yritysasiakkaisiin, viranomais- ja turvallisuuskriittisiin verkkoihin sekä 5G-ytimiin.
Toimitusjohtaja Börje Ekholm totesi, että RAN-markkinan vaisu kehitys jatkuu. Ericsson aikoo vastata tilanteeseen lisäämällä panostuksia puolustussektorille ja jatkamalla kulurakenteen optimointia. Tavoitteena on turvata kannattavuus ja kassavirta myös heikossa investointiympäristössä.
Vuoden 2025 viimeinen neljännes osoitti yhtiön mukaan strategian toimivan. Liikevaihto laski 5 prosenttia valuuttavaikutusten vuoksi, mutta orgaaninen kasvu oli 6 prosenttia. Kasvu tuli enterprise- ja mission critical -ratkaisuista sekä 5G core -liiketoiminnasta.
Alueellisesti kehitys oli kaksijakoista. Euroopassa, Lähi-idässä ja Afrikassa myynti kasvoi 7 prosenttia, mikä johtui erityisesti viranomaisverkkojen kysynnästä. Kaakkois-Aasiassa myynti kasvoi 6 prosenttia Vietnamin kiihtyneiden 5G-investointien ansiosta. Amerikassa myynti laski 11 prosenttia kovan kilpailun ja asiakkaiden verkko-investointien vähenemisen vuoksi. Koillis-Aasiassa pudotus oli 27 prosenttia.
Tomi Engdahl says:
‘Starlink killer’: China’s 20 GW microwave weapon could fry satellites with 60-second bursts
The compact microwave beam technology could disrupt satellite operations in low Earth orbit all the way from the ground.
https://interestingengineering.com/space/china-microwave-weapon-fry-satellites
Tomi Engdahl says:
Ericsson and Nokia see their sales in China fall off a cliff
Revenues generated in the China region by Ericsson and Nokia fell sharply last year as geopolitics continued to intrude.
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ericsson-and-nokia-see-their-sales-in-china-fall-off-a-cliff
Tomi Engdahl says:
Quantum-inspired wireless technology could tackle 6G’s biggest challenges
https://techxplore.com/news/2026-02-quantum-wireless-technology-tackle-6g.html
This research could enable faster and more reliable 6G wireless in homes, offices and public spaces, while powering smarter devices that run cooler and use less energy.
Professor Thas Nirmalathas, a pioneer in optical wireless communications at the University of Melbourne, said the team’s innovation uses modular optical phased arrays inspired by principles from quantum physics.
“The research combines quantum-inspired design with optical wireless innovation to tackle key challenges in the design of next-generation ultra broadband wireless systems,” Professor Nirmalathas said.
“Networks built this way can also adapt and grow with future technology demands. Building networks from flexible, reconfigurable blocks allows wireless systems to focus signals precisely where they are needed, reduce interference through polarization control, improve energy efficiency, and scale easily without redesigning entire networks.”
Tomi Engdahl says:
Breakthrough wireless transceiver transmits data 24 times faster than 5G connections, reaching blazing 15 gigabytes per second — Researchers demo invention that uses silicon chip to directly send and receive analog signals from digital data
News
By Jowi Morales last updated January 25, 2026
The future is analog.
https://www.tomshardware.com/networking/researchers-build-a-wireless-transceiver-that-can-transmit-data-at-15-gigabytes-per-second-24-times-faster-than-5g-connections-invention-uses-silicon-chip-that-sends-and-receives-analog-signals-from-digital-data-directly
Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have developed a transceiver that works in the 140 GHz range and can transmit data at up to 120 Gbps, that’s about 15 gigabytes per second. By comparison, the fastest commercially available wireless technologies are theoretically limited to 30 Gbps (Wi-Fi 7) and 5 Gbps (5G mmWave). According to UC Irvine News, these new speeds could match most fiber optic cables used in data centers and other commercial applications, usually around at 100 Gbps. The team published their findings in two papers — the “bits-to-antenna” transmitter and the “antenna-to-bits” receiver — on the IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Cohere Technologies fights to keep 6G doors open for something new
Incumbents have been describing 6G as an ‘evolution’ of 5G, but telco-backed Cohere Technologies wants a shake-up.
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/cohere-technologies-fights-to-keep-6g-doors-open-for-something-new
Tomi Engdahl says:
SpaceX Eyes 1 Million Satellites for Orbital Data Center Push
Updated Jan 31, 2026
In a late Friday FCC filing, the company mentions deploying a staggering ‘one million satellites’ in orbits ranging from 500 kilometers to 2,000km.
https://uk.pcmag.com/networking/162894/spacex-eyes-1-million-satellites-for-orbital-data-center-push
Tomi Engdahl says:
3G-verkko oli paras, älypuhelimella on vaikea soittaa – Yle kysyi asiantuntijoilta, pitävätkö yleiset väitteet paikkansa
Asiantuntijoiden mukaan huonoon kännykkäkuuluvuuteen on useita syitä, eikä vika ole aina verkossa.
https://yle.fi/a/74-20207493
Juttu tiivistettynä
Asiantuntijoiden mukaan syyt kännyköiden huonoon kuuluvuuteen ovat harvoin itse verkossa.
Esimerkiksi 3G-verkon alasajo ei heikentänyt yhteyksiä, sillä uudemmat 4G- ja 5G-verkot ovat tehokkaampia.
Kuuluvuutta heikentävät todellisuudessa energiatehokkaat rakennukset, puhelinmallien erot tai jopa puut.
Tuulivoimalat ovat poikkeus, ja ne voivat tutkitusti aiheuttaa häiriöitä verkon toimintaan.
3G-verkon alasajo on heikentänyt kuuluvuutta
Traficom:
3G‑verkon alasajo on joissain tilanteissa voinut paikallisesti heikentää kuuluvuutta. 3G:ltä vapautuneista taajuuksista suuri osa on otettu 4G- ja 5G-verkkojen käyttöön, mikä on parantanut verkkojen kapasiteettia ja palvelun laatua: käyttöönotto jatkuu edelleen lähivuosien aikana. Suomessa 4G- ja 5G-verkot ovat erittäin kattavia, ja kuuluvuusongelmiin on muitakin syitä kuin 3G:n poistuminen.
Telia:
Väite on yllättävä. Minullekaan ei ole aina niin selvää, missä verkossa puhelin kulloinkin on, joten kuinka ihmiset olisivat huomanneet juuri 3G:n puuttuvan. 3G:n alasajon aikaan jo 99 prosenttia käyttäjistä käytti 4G-verkkoa, jolloin heitä ei verkon sammutus koskenut.
3G-verkko oli parempi ja kattavampi kuin uudemmat verkot
Traficom:
4G-verkko on 3G-verkkoa kehittyneempi ja tarjoaa muun muassa nopeammat datayhteydet ja lyhyemmän vasteajan. Joissain tapauksissa 3G-verkko on voinut kattaa hieman isomman alueen 4G-tukiasemaan nähden: erot tulevat esille verkon peittoalueen reuna-alueilla.
Telia:
3G-, 4G- ja 5G-verkot toimivat hyvin samankaltaisesti, vaikka teknisiä toteutuseroja on.
Usein on turhaan epäilty, että 3G:llä olisi ollut parhaat taajuudet kuulua sisätiloissa. Kaikilla operaattoreilla on hyvät taajuudet 4- ja 5G-verkkojen käyttöön. Taajuudet ovat alhaisemmat kuin 3G:llä, joten niiden kuuluvuus on vähintäänkin yhtä hyvä ellei hieman parempi kuin aiempien 3G-taajuuksien.
Puhelimen kuuluvuus on viime aikoina vain heikentynyt
Traficom:
Rakentamistekniikka voi selittää havaintoja osittain sisäkuuluvuudessa. Tutkimusten mukaan tiiviin ja energiatehokkaan uudis- ja korjausrakentamisen on havaittu aiheuttavan kuuluvuusongelmia sisätiloissa.
Telia:
Verkkoon on lisätty tukiasemia ja kapasiteettia, eivätkä verkon testaukset tue ajatusta heikkenemisestä. Myöskään tukiasemissa ei ole kuluvia tai ajan myötä heikkeneviä osia.
Sen sijaan ajatusta voivat selittää muutokset ympäristössä tai vastaanottavassa päässä. Ihmiset vaihtavat puhelimia, signaalien tielle rakennetaan taloja, vaihdetaan vastaanottoa estäviä selektiivilasi-ikkunoita tai puut kasvavat.
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://phys.org/news/2026-02-topological-antenna-pave-6g-networks.html
Tomi Engdahl says:
DNA:n teknologiajohtaja: 6G tulee matkapuhelinverkoissa käyttöön pehmeästi
Teleoperaattori DNA uskoo verkkoliikenteen määrän kasvavan jatkossa rajusti. Silloin tiedonsiirtoon tarvitaan uudet tekoälyä hyödyntävät 6G-verkot.
https://www.lapinkansa.fi/dnan-teknologiajohtaja-6g-tulee-matkapuhelinverkoi/12518918
Teleoperaattori DNA aikoo olla aktiivisesti mukana visioimassa tulevaisuuden matkapuhelinverkkojen käyttöä.
Norjalaisen Telenorin omistama DNA on ainoana operaattorina mukana vuoden 2026 alussa alkavassa Oulun yliopiston vetämässä 6G Rocket -hankkeessa.
6G Rocket on yliopiston 6G Flagship -ohjelman alla toteutettava, kaksivuotiseksi suunniteltu tekoäly- ja radioverkkoteknologioihin (AI-RAN) keskittyvä kehityshanke.
Tomi Engdahl says:
6G could sense people and cars like radar, transforming connectivity into real-time awareness.
The next-generation mobile networks that will map movement in real time
6G networks could double as high-precision sensors, capturing the movement of people and cars similar to radar, but hurdles must be overcome to speed progress of research.
https://www.nature.com/articles/d42473-025-00379-1?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=APSR_SPOTL_AWA1_GL_PCFU_CFULF_SS-NTT-AP26&fbclid=IwdGRjcAP_0vhleHRuA2FlbQEwAGFkaWQBqy874efynHNydGMGYXBwX2lkDDM1MDY4NTUzMTcyOAABHiuU8OkMT4H0AqxSiS3XzQpbJWS5iJDHTT7ton4McthVdufDCObeZM-JGUCA_aem_kAyWcWWwW4ZGrC5ldxZdSg&utm_id=120241748762640572_v2_s09&utm_content=120241748762650572&utm_term=120241748762660572
Mobile networks may soon do more than help us make phone calls and access the Internet. They have the potential to be used as high-resolution sensors capable of detecting things in the environment, including people, cars or drones.
Integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) technology repurposes the signals continuously transmitted by cell phone towers. By analysing subtle distortions in radio waves as they travel through the air and reflect off objects, ISAC systems can detect the presence and movement of obstacles, similar to radar.
Researchers expect it to become one of the defining features of the next generation of so-called 6G networks, planned for release around 2030.
“With ISAC, sensing will be possible essentially anywhere with a signal,”
On 6G networks, ISAC will become far more powerful. While 4G mainly relies on sub-6 GHz bands, and 5G extends from mid-band (around 3–7 GHz) up to millimetre-wave frequencies near 30-40 GHz, 6G is expected to use even higher sub-THz bands above roughly 90–100 GHz, enabling much higher-resolution sensing.
The wider 6G bandwidths will soon enable the precise mapping of objects and movement at the millimetre level within the reach of signals from base stations. This could allow for capturing gestures as small as the wave of a hand without sensing equipment nearby.
While this may raise questions about privacy, ISAC systems are lower risk, say some experts, as they do not capture images directly like cameras, or as many identifying features of individuals.
“The first real-world applications for ISAC will probably be for presence detection of intruders and moving objects such as cars” says Ogawa
Full test setups that mimic commercial networks are expensive, and, because their internal designs are proprietary, researchers cannot modify waveforms that commercial base stations transmit into sensing-friendly forms.
In contrast, research using Wi-Fi and similar sensing principles has progressed more quickly because it operates on unlicensed bands. Individual laboratories are free to set up access points indoors and can freely experiment with how movement affects the shape and timing of radio waves. These studies have produced promising results for detecting motion within reach of Wi-Fi access points like homes and offices.
The vast coverage of cellular signals is unrivalled, and Wi-Fi signals weaken over longer distances. “If we want to transform the scale at which we sense things, we also need mobile networks,” says Murakami.
A recent study by Murakami, Ogawa, and colleagues, showed that ISAC can be studied in the real world without transmitting signals1. The team used low-cost hardware to capture commercial signals and combined it with open-source software to interpret their structure.
Using an antenna to receive signals and their changes, their experiment compared when no one was in front of the antenna, and when a person walked across its line of vision at various distances.
On analysing changes to the signals, the team found that their system could reliably detect a person walking outdoors at distances of up to 10 metres. Sensing a combination of different frequency ranges, rather than focusing on a single one, covered for blind spots in each range and improved accuracy.
Murakami explains that organizations are keen to detect the general numbers of people in a given area and the flow of crowds in real-time. For example, public authorities could refer to these insights during large-scale events, such as festivals, to facilitate visitor flow. From a commercial perspective, the data can also be utilized to gathering marketing insights such as measuring event success.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Beyond 6G networks
What will it take to move beyond 5G? In this guide, VTT explores the key technologies and research shaping the shift towards 6G and beyond.
https://www.vttresearch.com/en/explore/beyond-6g-networks?gad_source=1&gad_campaignid=22803316754&gclid=Cj0KCQiAhtvMBhDBARIsAL26pjHYBZlZ34VU7NE1l5PAUfvLYkVM8mjT-mQr7GKvdLlrc9Fb0ly3GAsaAo7eEALw_wcB
Discover how AI-driven network management, edge computing, advanced RF components, and silicon photonics will enable secure, high-performance and energy-efficient 6G networks. Learn why open architectures like O-RAN are essential for future scalability and resilience.
Download the white paper to explore VTT’s vision and cutting-edge research powering the next generation of connectivity!
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.oreateai.com/blog/unpacking-the-1g-cellular-system-the-analog-dawn-of-mobile-communication/5f9f7b590d1f53b07b377d2ccf6f3f6a
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18609-nokia-ja-ericsson-tiivistaevaet-yhteistyoetae-autonomisissa-verkoissa
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/18626-nokia-kaeyttaeae-joka-neljaennen-euronsa-tutkimukseen
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2026/03/04/mwc2026-suomi-tiivistaa-6g-turvallisuusyhteistyota/
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2026/03/05/tulevaisuuden-radiotaajuudet-seminaarissa/
Tomi Engdahl says:
Ericsson completes pre-standard 6G trial in US, ties up with Qualcomm
“6G will be foundational to how artificial intelligence scales across society and will be critical to the national security, economic prosperity, and global competitiveness of the United States,” said Borje Ekholm, president & CEO, Ericsson.
https://telecom.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/telecom-equipment/ericsson-completes-pre-standard-6g-trial-in-us-ties-up-with-qualcomm/128872317
NEW DELHI: Swedish telecom gear maker Ericsson said on Friday that it has succes ..
Read more at:
https://telecom.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/telecom-equipment/ericsson-completes-pre-standard-6g-trial-in-us-ties-up-with-qualcomm/128872317
Tomi Engdahl says:
Why Nokia Oyj (HLSE:NOKIA) Is Up 7.7% After Launching 5G Core SaaS With Citymesh and AWS
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/why-nokia-oyj-hlse-nokia-171031725.html
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/t-mobile-tests-6g-with-ericsson-prototypes