Another bad and potentially dangerous circuit from Facebook.
This is supposed to charge LiIon battery from USB power. Identified problems:
- no current limiting
- can overcharge the battery
- red charging LED will be always on when there is USB power coming in
- green charged LED will not turn on when battery is full
This circuit, as drawn, will not work properly or safely for charging a 3.7 V Li-ion battery. In this circuit, there is nothing to limit the charging voltage/current properly. The battery may overcharge (risk of fire or explosion).
The diode blocks the backflow voltage when the USB power is off and provide 0.7 voltage drop. The design intention seems to be that this would limit the battery charging voltage to safe level.
But even with the diode you have 5V from USB, minus 0,7V over the diode, that is still 4,3V, which is too much for the LiIon battery. So battery will be overcharged.
The typical maximum safe voltage for a standard Li-ion battery cell is 4.20V, although some higher-voltage chemistries can reach 4.30V. Charging a cell above its maximum voltage can cause irreversible damage, shorten its lifespan, and compromise safety. Battery management systems (BMS) in Li-ion packs prevent overcharging and ensure the voltage remains within safe limits. This simple circuit is not proper BMS.
The USB standard specifies a nominal 5V supply but allows for a voltage range between 4.75V and 5.25V for standard USB power delivery, with some USB 2.0 and 3.x specifications permitting higher voltages up to 5.5V to account for voltage drops. If your USB power supply gives those over 5V voltage, we are very considerably over the allowed maximum voltages.
Lithium batteries need constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV) charging, typically limited to 4.2 V max with current control.
LED “full” and “charging” indicators won’t function correctly. The green/red LEDs with just a resistor and diode cannot sense charge status. The LED will just glow depending on voltage drops, not actual battery full/charging state. Because it shares resistor with red LED, it will not be on when red LED is on.
If you want to charge a 3.7 V Li-ion battery from USB, you need:
A TP4056 charging module (very cheap, <$1). It provides correct CC/CV charging. It includes overcharge, over-discharge, and short-circuit protection (if you buy the protection version).
Comes with proper red/blue LEDs for charging/full indicators.
Another bad battery charger circuit. Lacking proper charging current limiting, proper control of charge stopping when battery is full, too much voltage drop on diodes to work well, green full LED can stay always on or not turn on at all depending green LED used (voltage drop can very between 1.9V and 4V on green LEDs)
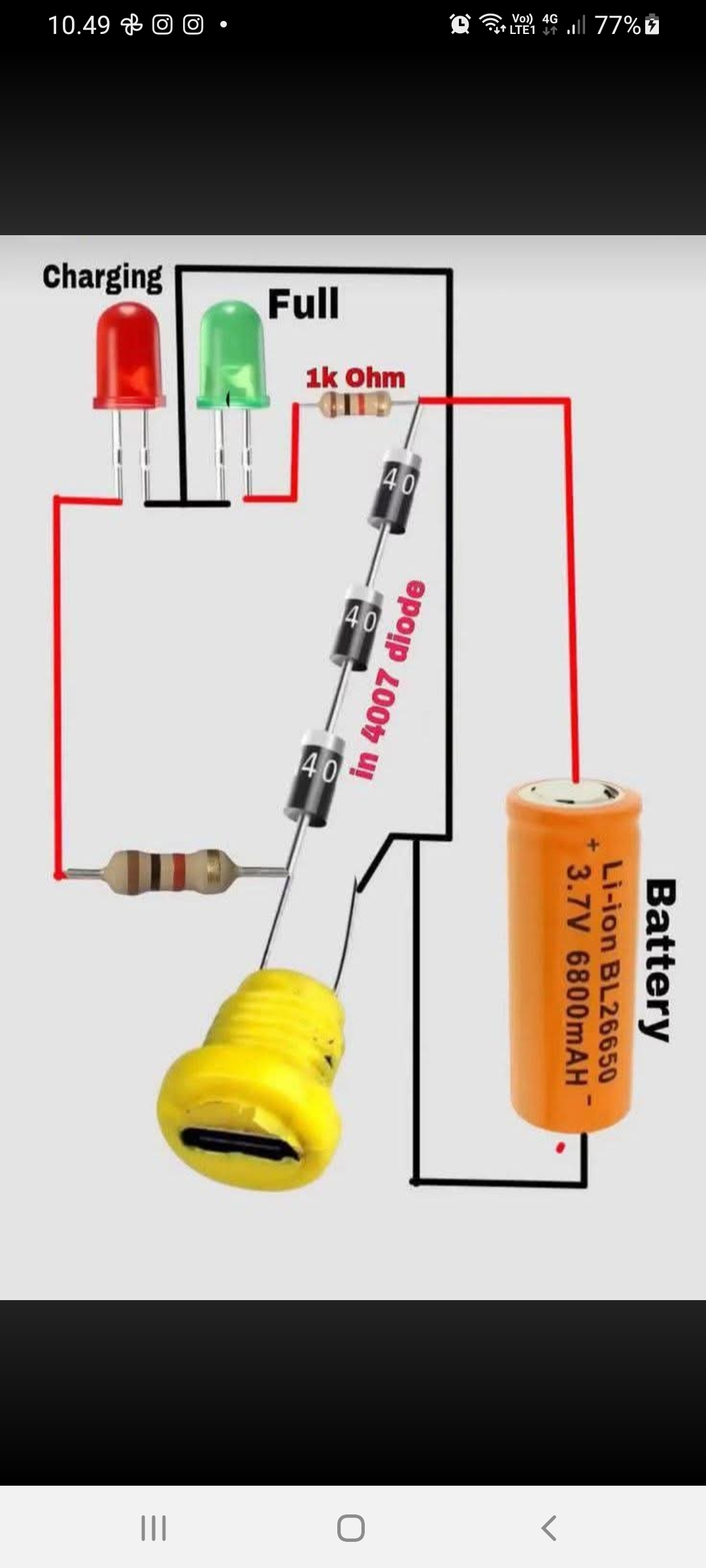
This claims to be a simple Li-ion battery charging indicator circuit.
It uses LEDs, resistors, diodes (1N4007), and a USB 5 V source to:
Charge a 3.7 V Li-ion battery, and
Indicate charging (red LED) and full charge (green LED) states. The 1N4007 diodes (3 in series) will get voltage drop (~0.7 V each × 3 = 2.1 V total). The battery gets a reduced voltage because of the voltage drops across the diodes, and the pproximate voltage at the battery terminals is around 2.9 that is not enough to properly charge the battery. The voltage drop over diodes will be lower at very low current, so a little bit current could get to battery.
This is a very basic indicator circuit, not a safe Li-ion charger.
It lacks:
Constant-current control (CC mode)
Constant-voltage regulation (CV mode)
Overcharge protection
Reverse polarity protection
Temperature monitoring
So while this circuit might be able show charging/full with certain not specified green LED, it’s not recommended for actual battery charging. Use a TP4056 module or similar dedicated Li-ion charger IC instead — it’s safer and inexpensive.
4 Comments
Shanaya says:
This article rightly condemns a poorly designed circuit for Li-ion battery charging from USB power, highlighting the severe safety and performance issues like lack of current limiting and potential overcharging (fire/explosion risk) due to inadequate voltage regulation. The conclusion HCTRA System Map is to use a dedicated, safe charging solution like a TP4056 module.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Congratulations for makes Facebook a worse place by posting a non-working AI crap circuit diagram
Tomi Engdahl says:
Voisi olla terveellistä, että kaikki rakentelijat tietäisivät, miten li-ion-akku ladataan.
Sille on syynsä, miksi jokaisessa lataavassa laitteessa on älykäs latauspiiri, joka huolehtii siitä, ettei akku räjähdä.
https://www.akkutohtori.fi/litium-akun-lataaminen/#:~:text=Laturin%20tulee%20olla%20tarkoitettu%20litium,ett%C3%A4%20k%C3%A4yt%C3%B6ss%C3%A4si%20on%20oikea%20laturi.
“Litium[-]akkua ladataan ensin vakiovirralla, kunnes akun jännite saavuttaa Maksimijännite arvon. Tämän jälkeen laturi lataa akkua vakiojännitteellä, kunnes akun latausvirta on pudonnut noin 10% alkuperäisestä vakiovirrasta.”
Tomi Engdahl says:
What does rage-bait mean? Rage-bait (also spelled as ragebait and rage bait) is content (usually, but not always, found online) that tries to provoke anger or outrage, as a means of gaining attention or making money. The word is also used as a verb (“to make intentionally provocative or inflammatory statements”).