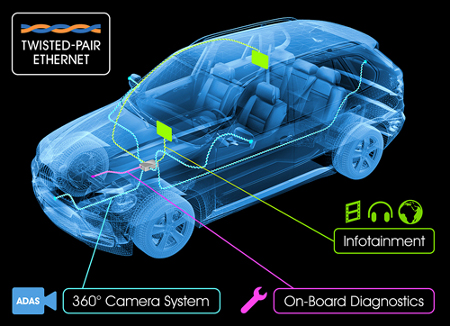
Ethernet for Vehicles Advances article tells that Ethernet technology in the car (a concept that was once unthinkable for the automotive industry) has been gaining momentum lately. The irony of this sudden trend is that a few years ago, Ethernet wasn’t seen as a solution to any applications in the car (one exception for this rule is that BMW cars supporting Ethernet have been on the market since 2008).
There are many existing in-vehicle technologies such as CAN, LIN, LVDS and FlexRay. Just few years ago MOST (Media Oriented Systems Transport) was seen as the de-facto standard for multimedia and infotainment networking in the automotive industry, but is has has now fallen out of favor. So now it seem to be right time for Ethernet.
A coalition of automakers and automotive suppliers said recently that they are forming a special interest group (SIG) aimed at driving broad-scale adoption of Ethernet in vehicles, largely to serve the expected boom of camera-based applications in cars. NXP and Broadcom are playing a big role in the launch of the new special interest group, known as the OPEN (One-Pair-Ether-Net) SIG. This SIG is focused on the idea of creating a single physical layer that would enable easy use of Ethernet with vehicle cameras. OPEN Alliance is designed to encourage wide scale adoption of Ethernet-based, single pair unshielded cable networks as the standard in automotive applications.
NXP said it would be the first supplier to license Broadcom’s BroadR-Reach ethernet technology (technology originally designed to extends the range of twisted pair connections from 100 meters to up to 500 meters) for in-vehicle networking. Broadcom has also introduced their Automotive Ethernet Product Portfolio. BroadR-Reach allows full-duplex operation over a single twisted pair at 100 Mbps (same type of cabling 80-110 ohms unshielded or shielded twisted pair cabling as used in FlexRay works).
Interest in one pair Ethernet technology has grown dramatically as the automotive industry accelerates its adoption of Ethernet based networks. BMW and Hyundai have teamed up with Broadcom, NXP Semiconductors, Freescale and Harman to make ethernet the computer networking technology of choice inside the car. Infotainment systems maker Harman said that higher-bandwidth connectivity will address customers’ growing demand for seamlessly integrated information, entertainment and safety features in the car.
I have been for long time wondering why the automotive makers have been very hesitant to spec Ethernet in the past since it’s such a well-proven technology? Ethernet has gained momentum in many sectors, because it’s a fast, mature technology with high production volumes in the computer industry. Now it is the time for the auto industry is to leverage the computer industry’s enormous Ethernet know-how.

135 Comments
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.3
Tomi Engdahl says:
Single-Pair Ethernet Comes Just in Time
March 2, 2022
Industrial facilities and automakers needed a cost-effective connectivity solution for low-data-rate devices, and 10BASE-T1S and 10BASE-T1L deliver it with low cost and simplicity.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/industrial-automation/article/21214176/microchip-singlepair-ethernet-comes-just-in-time
Tomi Engdahl says:
Meeting the Challenge of Ethernet System Validation
Aug. 6, 2018
As data becomes as important to modern vehicles as oil and gasoline were in the past, simulators will provide the assurance that every vehicle operates at peak performance.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21806837/meeting-the-challenge-of-ethernet-system-validation
Cars and trucks are quickly becoming Formula One race cars—at least in terms of data. With more types of onboard devices requiring near-instantaneous data transmission than ever before, engineers and designers are challenged to accommodate the accelerating need for bandwidth and speed.
At the core of just about every innovation today, from advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to collision detection sensors and infotainment systems, is data. Traditional automotive data networking technologies such as controller area networks (CANs), local interconnect networks (LINs), and Media Oriented Systems Transport (MOST) were not designed to support the bandwidth these systems demand. In fact, the need to implement time-sensitive networking (TSN) standards has forced engineers to look outside the automotive arena for alternative transit solutions.
Ethernet is the obvious choice. This staple of the IT world, while not exactly new to automobiles, is being applied with increasing frequency, and for a number of reasons. Ethernet technology allows for fewer cables of lighter weight—not an insignificant advantage. Also, automotive engineers know that Ethernet is proven technology, supported by many device manufacturers, and has a strong hardware/software support ecosystem.
Yet Ethernet can’t satisfy all requirements for data networking performance—which is why there’s also a need for TSN technology. TSN guarantees that high-quality data packets are delivered with low latency, something Ethernet doesn’t natively support. In addition, TSN provides a network-wide clock for packet synchronization across systems, and prioritizes time-sensitive data streams over those of lower priority. Finally, it guarantees a minimum level of availability for emergency transmission.
Validating high-speed Ethernet devices for automotive use is a complex undertaking.
Automakers, along with in-vehicle device and system OEMs, have stringent requirements for latency, synchronization, conformance, availability, and QoS. These requirements must be met, as consumers must be able to rely on their cars and trucks for safe, reliable performance. The potential cost of failure—not to mention recalls, liability, and damaged reputations—is simply too high.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Autojen uusi verkko siirtää 50 gigabittiä sekunnissa
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/13429-autojen-uusi-verkko-siirtaeae-50-gigabittiae-sekunnissa
Takana ovat ne päivät, kun autoissa riitti CAN-väylä kaikenlaisen datan siirtoon. Nyt tulollaan on 802.3cz-standardi, joka on edennyt IEEE:ssä jo äänestysvaiheeseen. Se nostaa autojen sisäisen optisen verkon nopeuden jopa 50 gigabittiin sekunnissa.
Autojen optisten verkkojen pioneereihin kuuluu espanjalainen KDPOF. Se lupaa esitellä 802.3cz-pohjaista ratkaisua jo Vehicle Electronics & Connected Services -messuilla Göteborgissa toukokuun puolivälissä.
Autoteollisuuden 802.3cz-standardiluonnos määrittelee nopeudet alkaen 2,5 Gb/s aina 50 Gb/s asti. IEEE:n 802.3-työryhmässä ovat mukana monet suuret autonvalmistajat, kuten PSA, Toyota, BMW, Ford, GM ja Volvo. Lisäksi mukana on kärkipään järjestelmä- ja komponenttien toimittajia.
Ehdotettu IEEE 802.3 autojen optinen monen gigabitin standardiluonnos määrittää 2,5, 5, 10, 25 ja 50 gigabitin GBASE-AU-määritykset OM3-luokan kuidulla. OM3-luokka on valittu, koska sitä käytetään jo laajasti datakeskuksissa, ja sitä käytetään myös monissa haastavien olosuhteiden kohteissa kuten ilmailutekniikassa.
Ehdotettu usean gigabitin järjestelmä herää alle 100 millisekunnissa.
Autoympäristön käyttölämpötila -40 ºC … +125 ºC (AEC-Q100 luokka 1) on perinteisiä verkkosovelluksia haastavampi, samoin kuin OEM-luotettavuusvaatimukset, joiden mukaan järjestelmän ja komponenttien pitää kestää käytössä vähintään 15 vuotta.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Ethernet yltää nyt 1,7 kilometrin päähän
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/13500-ethernet-yltaeae-nyt-1-7-kilometrin-paeaehaen
Analog Devices on tuonut markkinoille täydellisen 10BASE-T1L Ethernet-ratkaisun, joka on suunniteltu rakennusautomaatioverkkoihin. Uusi ADIN2111 lisää pitkän ulottuvuuden Ethernet-liitettävyyden ohjaimiin, antureihin ja toimilaitteisiin, mikä tarjoaa oivalluksia tehokkaampaan ja kestävämpään kiinteistönhallintaan.
Piiri on suunniteltu datan ketjuttamiseen linja- ja rengasverkoissa käyttämällä olemassa olevaa yhden kierretyn parikaapelin infraa rakennuksissa.
Tämä IEEE 802.3cg -standardin mukainen ratkaisu mahdollistaa Ethernet-yhteyden yli 1,7 kilometriä kaapelointia, tukee soittojen redundanssia ja pehmeitä reaaliaikaisia protokollia, kuten Modbus/TCP, BACnet/IP ja KNX.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Moving from Domains to Zones: The Auto Architecture Revolution
May 24, 2022
A new approach is needed in automotive interconnection architectures—a fundamental shift in the way hardware and software functions are partitioned across newly configurable platforms.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21242583/nxp-semiconductors-moving-from-domains-to-zones-the-auto-architecture-revolution?utm_source=EG+ED+Auto+Electronics&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS220517098&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.ident%5Bpull%5D=omeda%7C7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
What you’ll learn:
The shift from conventional electrical and electronic (E/E) architecture within the vehicle to the domain and zonal architectures.
How software is taking precedence over hardware in defining the vehicle and its key components.
How automotive manufacturers are now moving from domain to zonal architectures.
Challenges with—and a solution to—the zonal approach implementation.
The wiring harness in many vehicles now weighs more than any other component, except the engine—whether it’s an internal combustion engine (ICE) or battery-powered electric motor. Reducing this unsustainable burden demands an entirely new approach to interconnection architectures, and it can’t be realized using high-speed serial buses and networking technologies alone.
To fully address the issue requires a fundamental shift in how hardware and software functions are partitioned across newly configurable platforms.
Dividing into Domains—and the Need for a Zonal Approach
Due to the increasing complexity of the conventional vehicle architecture caused by the addition of more and more electronic control units (ECUs), an alternative approach was introduced to add structure and hierarchy. The approach was to divide the vehicle into “domains,” or areas with common functionality—such as the chassis, powertrain, body & comfort and infotainment, and ADAS—and connect them to a centrally located service-oriented gateway via a dedicated domain controller
Challenges in Zonal-Approach Implementation
While the automotive industry has relied on CAN networking for decades, it’s becoming apparent that it’s unable to cope with the demands of vehicles today. This is especially the case for the “backbones” that connect the zonal gateways, which will be based on Ethernet. However, the hierarchical nature of the zones will introduce more “hops” within the network, potentially causing latency and jitter issues.
Many of the systems in a modern vehicle have time dependencies, which is especially critical in safety-related systems, such as ADAS. While a delay in opening a window or changing a radio station would be an inconvenience, a delay to a message from a camera that has detected an obstruction resulting in brakes being applied late is potentially catastrophic.
This highlights a weakness of traditional Ethernet in that data packets are only propagated when the backbone is free of other traffic, and there’s no hierarchy of relative importance. Simply put, traditional Ethernet would see a data packet for changing a radio station as equally important as one to apply the brakes.
In-vehicle networking will be based on IEEE 802.1AS-2020, the IEEE-approved standard for timing and synchronization in time-sensitive networking (TSN) applications. Often called “deterministic Ethernet,” this standard includes several features for ensuring that data is managed to strict time criteria based on the importance of the data, including ensuring that time-sensitive traffic is propagated via the shortest path.
This high-speed Ethernet will form the backbone of the zonal architecture and connect zone controllers with one another as well as with the central computing resources. However, things will become more complex within each zone due to multiple types of edge networks being implemented, connecting the zone controller to various edge ECUs. While Ethernet may be used in some cases, a significant amount of CAN infrastructure will exist in both CAN (FD) and CAN XL formats.
Several areas should be considered for this multi-protocol approach to work effectively. In particular, the designer must consider how data is moved onto and from the Ethernet backbone to and from the in-zone network. This is further complicated by the fact that CAN traffic is typically periodic and broadcast, compared to Ethernet, which is usually event-based and point-to-point.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Broadcom Delivers World’s First 50G Automotive Ethernet Switch
https://www.broadcom.com/company/news/product-releases/60241
Industry’s highest bandwidth switch solution enables efficient zonal and central compute platforms and accelerates adoption of software defined vehicles
SAN JOSE, Calif., May 23, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Broadcom Inc. (NASDAQ: AVGO) today announced it has delivered its high bandwidth monolithic automotive Ethernet switch device, the BCM8958X, designed to address the growing bandwidth need for in-vehicle networking applications and facilitate the adoption of software defined vehicles (SDV). The BCM8958X features 16 Ethernet ports of which up to six are 10 Gbps capable, as well as integrated 1000BASE-T1 and 100BASE-T1 PHYs, providing greater flexibility and switching capacity needed to support automotive zonal electronic control unit (ECU) and central compute ECU architectures. Additionally, this switch is equipped with an advanced rule-based packet filter engine that can adapt to different vehicle operation modes to enhance driving safety.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Autoihin tulee gigabitin optinen verkko
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/14036-autoihin-tulee-gigabitin-optinen-verkko
Autojen sisäisissä verkoissa datan nopeus- ja kapasiteettivaatimukset kasvavat koko ajan. Perinteinen CAN ei jatkossa enää riitä ja sen tilalle ovat tulossa nopeammat Ethernet- ja kuituratkaisut
Espanjalainen KDPOF kehittää optisia kytkinratkaisuja myös ajoneuvoihin. Nyt yritys on yhdessä NXP Semiconductorsin kanssa esitellyt ensimmäisen evaluointikortin, jolla voidaan tetata gigabitin optista verkkoa ajoneuvossa. Alustan on tarkoitus vastata tulevaisuuden verkkoon kytkettyjen autonomisten ajoneuvojen tarpeisiin.
KDPOF:n ensimmäinen autoihin kehitetyssä Ethernet-kytkimessä (EVB9351-AUT-SW-NXP) on viisi 1000BASE-RH optista porttia, joista jokainen koostuu KDPOF:n KD9351 FOT- ja KPHDY10533-porteista. Kytkinpiirit (SJA1110) tulevat NXP:ltä. Ne perustuvat Arm Cortex-M7 -prosessoreihin.
512 kilotavun laiteohjelmistolla kytkin käynnistyy alle 100 millisekunnissa.
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.kdpof.com/first-automotive-gigabit-ethernet-switch-with-optical-ports/
Tomi Engdahl says:
What’s the Difference Between CAN and SPE in the Automotive Industry?
Jan. 6, 2023
The CAN bus protocol is being phased out of the automotive industry in favor of single-pair Ethernet due to its increased data bandwidth, node efficiency, security, and more.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21257559/electronic-design-whats-the-difference-between-can-and-spe-in-the-automotive-industry?utm_source=EG+ED+Auto+Electronics&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230119091&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
What you’ll learn:
How single-pair Ethernet is taking over for CAN bus.
How SPE improves on CAN.
It’s been 36 years since the CAN (controller area network) bus was released by the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers). Lying at the heart of vehicle communications for decades, it supports a wide variety of automotive innovations.
The CAN bus is described as a vehicle bus standard that allows microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other’s applications without a host computer. It’s a message-based protocol, designed originally for multiplex electrical wiring within automobiles to save on copper, but it also can be used in many other applications.
Automotive technology has come a long way since the first CAN buses were deployed, and the platform has since been tasked with more and more functions beyond what was envisioned in the 1980s.
CAN remains a favorite of auto manufacturers even into its fourth decade. That said, the automotive industry has been undergoing a paradigm shift in response to cutting-edge technologies and fast-evolving consumer demands. CAN’s long-running reign is set to face new challenges.
To that end, the automotive industry is looking toward single-pair Ethernet (SPE) to function as the automotive network’s backbone, an alternative that brings higher performance, increased security, and increased efficiency over CAN buses.
According to a 2020 market report, the global connected-car market is expected to reach $225.16 billion by 2027, up from $63.03 billion in 2019. This shift toward increased connectivity will play a decisive and accelerating role in the move to SPE networks, even as CAN buses continue to provide an important communication medium (primarily for legacy components).
Tomi Engdahl says:
Simplify Automotive Networks for Real-Time Driver Assistance
March 8, 2023
Sponsored by Texas Instruments: FPD-Link SerDes technology is equipped to readily handle the massive amounts of data transferred in ADAS systems.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/tools/learning-resources/whitepaper/21260142/texas-instruments-simplify-automotive-networks-for-realtime-driver-assistance?pk=DesEssen-03162023&utm_source=EG+ED++Sponsor+Paid+Promos&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230314034&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
In the automotive industry, technologies that influenceadvanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are evolving rapidly. Applications range from basic vehicle functions such as lighting, braking, and cruise control to more complex uses like engine and transmission control, traffic warnings, proximity to other cars, and correct lane use.
Because highly automated and connected cars will rely on more than one type of network architecture, designers are being challenged to employ multiple network technologies simultaneously. The goal is to communicate critical information in real-time and with precision to keep drivers informed about operational data and the status of the vehicle.
In the automotive industry, technologies that influenceadvanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are evolving rapidly. Applications range from basic vehicle functions such as lighting, braking, and cruise control to more complex uses like engine and transmission control, traffic warnings, proximity to other cars, and correct lane use.
Because highly automated and connected cars will rely on more than one type of network architecture, designers are being challenged to employ multiple network technologies simultaneously. The goal is to communicate critical information in real-time and with precision to keep drivers informed about operational data and the status of the vehicle.
Communication Protocols in
Modern ADAS Architectures
https://www.ti.com/lit/wp/slyy219/slyy219.pdf?HQS=null-null-adas-adascomm-asset-whip-electronicdesign_03-wwe_awr&DCM=yes&dclid=CIjS1anP4v0CFQKMmgodlpQPJA
The modern vehicle relies on high-speed automotive
communication technologies that move data faster and
farther to accelerate vehicle safety and autonomy.
Ethernet
Ethernet is one of the most common high-speed
interfaces found in homes and offices, and is becoming a
predominant communication protocol for vehicles. Some
vehicles use Ethernet to transport a variety of high-speed
data; automotive applications such as radar and lidar
modules use single-pair Ethernet technology. Single-pair
Ethernet uses the Ethernet standard, but data transmits
over a single, twisted pair of wires, enabling reduced
cable weight and cost within the vehicle.
Ethernet is a packetized system, where packets
between nodes on various parts of the network
transfer information. Also like a CAN bus, Ethernet is
bidirectional, and the speed possible on any individual
link decreases as the number of nodes on the system
increases. For single-pair Ethernet, the speed on any
individual link is limited to one specific speed (10 Mbps,
100 Mbps, 1 Gbps) and no dynamic speed changes
on the link may occur. Still, single-pair Ethernet can
transport data over a link up to 1,000 times faster than
a CAN bus. Changing to single-pair Ethernet would
optimize the data transmission speed over a CAN bus,
but since Ethernet’s cost per node is higher, it probably
will not replace – but rather will augment – a CAN bus.
Some cars today use single-pair Ethernet for data-
intensive requirements such as backup cameras
and radar. For example, the DP83TC812S-Q1 and
DP83TG720S-Q1 from Texas Instruments (TI) are single-
pair Ethernet physical layers (PHYs), screened to
Automotive Electronics Council-Q100 grades 1 and
2, and include a loopback test mode for facilitating
system diagnostics compliant to Institute of Electrical
and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.3bw and 802.3bp
automotive standards. To transport video over an
Ethernet network, even if there is only one video channel
being transported, the video must be compressed at
its source and then decompressed at the destination
to avoid exceeding Ethernet bandwidth limitations unlike
FPD-Link™ technology, which allows for uncompressed
transport of video data. For an application such as
a backup camera, there needs to be a relatively high-
power processor in the camera to compress the image
sufficiently to get it into the Ethernet network.
The need for a high-power processor in turn means
that the camera will be physically larger and more
expensive. The camera will have a higher power
dissipation than an approach that does not require
much image processing. Another disadvantage of this
solution is that video compression and decompression
add latency to the link. If several cameras or other
video sources are sharing the same Ethernet network,
there is a trade-off between the amount of compression
(and corresponding video quality) and the number of
supported video channels. It is possible to mitigate this
limitation by setting up multiple networks within the car in
a hierarchical configuration. There might be one network
that deals only with engine control and diagnostics, a
second network that handles backseat entertainment
and the audio system, and another network that handles
driver assistance functions such as vision enhancement
cameras. In the end, single-pair Ethernet provides higher
capacity than the CAN bus for transmitting data like
radar and lidar, at the expense of greater complexity,
but still struggles to handle the highest-bandwidth
applications such as video.
FPD-Link technology
FPD-Link is a proprietary automotive SerDes technology
developed for real-time, uncompressed transmission
of high-bandwidth data. Specifically, FPD-Link was
developed to transport video data within the car,
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://incompliancemag.com/article/verifying-the-effect-of-electromagnetic-noise-on-an-in-vehicle-ethernet-network/
Tomi Engdahl says:
Control Unit Uses TSN to Take Vehicle Networking to Next Level
As automakers take the next steps toward the software-defined vehicle, which can be upgraded with new services and features remotely over time, they require high-speed in-vehicle networks to match.
TTTech launched a high-end electronic control unit (ECU) with time-sensitive networking (TSN) and other advanced networking features that acts as a secure central gateway to wire together different domains in the car and relay data from around the car to the cloud. In the future, it can also act as a central computer in a hybrid or zonal architecture.
Based on NXP’s high-end S32G network processor, the N4 Network Controller supports a wide range of Ethernet, CAN-FD, CAN, and LIN bus interfaces. It adds several gigabytes of flash memory, enabling over-the-air software updates over time. TTTech said the unit comes with everything to keep the vehicle secure from hackers according to ISO 21434, while also allowing for functional-safety features up to the ASIL B rating under the ISO 26262 standard.
The combination of the dual Arm Cortex-A53 and the Cortex-M7 CPU clusters supports both high-performance and functional safety in a single ECU. At the same time, different operating systems, such as AUTOSAR Classic and Linux, can run in parallel.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/resources/products-of-the-week/media-gallery/21265339/electronic-design-products-of-the-week-sicbased-power-supply-io-link-analog-converters?utm_source=EG+ED+Analog+%26+Power+Source&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230504032&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R&id=21265339&slide=2
Tomi Engdahl says:
Uusi standardi tuo 50 gigabitin optiset verkot autoihin
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/15125-uusi-standardi-tuo-50-gigabitin-optiset-verkot-autoihin
IEEE on saanut valmiiksi Ethernet-standardin, joka tuo jopa 50 gigabitin optiset yhteydet ajoneuvoihin. Standardi on nimeltään IEEE 802.3cz-2023 ja sen fyysinen osa tukee nopeuksia 2,5 Gb/s, 5 Gb/s, 10 Gb/s, 25 Gb/s ja enimmillään 50 gigabitin sekunnissa.
IEEE 802.3cz-2023 (nGBASE-AU) -standardi on suunniteltu alusta alkaen siten, jotta se täyttää tiukat autoteollisuuden vaatimukset. Optisen kuidun käyttö pienentää merkittävästi virrankulutusta. Lisäksi se pitää pintansa pitkälle tulevaisuuteen, koska autojen ECU-yksiköt voidaan päivittää suuremmille nopeuksille säilyttäen samat johtoasemat.
Jatkossa autoon saadaan 25 tai jopa 50 gigabitin optinen verkko yhdellä OM3-multimedia-kuitukaapelilla ja 4 liittimelllä. Yhteys yltää 40 metrin päähän, mikä riittää auton tarpeisiin monin verroin.
Standardi täyttää autojen lämpötilavaatimukset (-40 °C … +105 °C) ja luotettavuusvaatimukset vähintään 15 vuoden käytölle.
Uuteen standardin perustuvat liitäntäratkaisut ovat edullisia, koska korkeampi optinen tehobudjetti mahdollistaa pienemmän toleranssin liittimet. Lisäksi OM3-kuitua käytetään laajasti, mikä varmistaa suuren volyymin tuotannon. Fyysinen kerros on yksinkertaisempi, joten siinä tarvitaan vähemmän DSP-virheenkorjausta, eikä erilliselle kaiunpoistolle ole tarvetta.
Suurempia nopeuksia varten autoteollisuuden vaatimukset edellyttävät tätä siirtymistä kuparista optiseen fyysiseen tiedonsiirtoon. Optinen Ethernet-yhteys ratkaisee täydellisesti ajoneuvojen haasteet ja sähköiset häiriöt lyömättömän sähkömagneettisen yhteensopivuuden, luotettavuuden ja alhaisten kustannusten ansiosta.
Tomi Engdahl says:
How 10BASE-T1S Can Drive Wider Adoption of Automotive Ethernet
July 5, 2023
The 10BASE-T1S standard for automotive Ethernet allows manufacturers to implement Ethernet-to-the-edge connectivity and optimize wireless connections to cloud services. However, suppliers must overcome hurdles before adopting it.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21268945/mouser-electronics-how-10baset1s-can-drive-wider-adoption-of-automotive-ethernet
What you’ll learn:
What is 10BASE-T1S and how does it work?
How 10BASE-T1S can benefit automotive systems and increase scalability in the industry.
The challenges that still need to be addressed before 10BASE-T1S is implemented across the entire automotive spectrum.
When CAN Can’t
As mentioned earlier, CAN tops out at 1 Mb/s, and the faster variant CAN-FD maxes out at 8 Mb/s. The limits are a serious impediment to a number of automotive capabilities that are already standard features as well as other proposed options. Data from cameras, radar, and LiDAR used in current collision-avoidance systems and other ADAS features demand far more bandwidth than is available through the CAN bus. For example, the data stream from a single LiDAR sensor can be upwards of 70 Mb/s.
The automotive industry needed a replacement for the aging CAN protocol and decided to adopt Ethernet to handle in-vehicle communication. Ethernet is widely used in data centers, manufacturing, home networks, and more to transfer large data throughput.
However, the auto industry uses another form known as automotive Ethernet (AE). Vehicles employ the AE protocol as it adds a physical layer for specific use cases, and the cost of the cables is reduced by using PHY transceivers that stand up to challenging road conditions. It provides a higher baud rate over traditional Ethernet and allows for the reuse of IP technologies from other industries.
AE supports data transfer at roughly a gigabit per second. Subsequent versions include IEEE 802.3cg, which specifies up to 10 Mb/s on a single pair, and 802.3ch, which specifies 2.5, 5, and 10 Gb/s, also on a single pair. AE ordinarily specifies the use of twisted-pair cables to reduce weight and costs, but fiber optics are typically more resistant to noise and more conducive to signal integrity.
That being said, automotive Ethernet isn’t without its challenges, as the demands for higher bandwidth increase as technology and applications evolve.
Several of those key challenges include maintaining multi-gigabit transmission of data within the vehicle in the near term while aiming for much higher throughput in the long term. Trying to maintain electromagnetic compatibility and reliability with increasingly noisy environments is another concern, along with maintaining low weights and costs associated with wire harnesses to support a data center on wheels.
Enter 10BASE-T1S
New IEEE automotive Ethernet standards are starting to emerge to address those challenges. One of the latest is 10BASE-T1S, which is designed to support new architecture rollouts.
10BASE-T1S, which is specified in the IEEE 802.3cg standard, defines a physical layer and data link layer for MAC addresses within Ethernet networks. The physical layer provides connections to nodes or devices such as routers, switches, and hubs.
Broken down, the “10” represents the maximum transmission speed (10 Mb/s), “BASE” refers to baseband signaling, and “T1” denotes single twisted-pair cabling. The specification is designed to provide a multi-drop transmission medium that can handle at least eight transceiver nodes or devices at distances of 25 meters or more. The “S” means a short length or short reach.
With 10BASE-T1S, standard Ethernet communication no longer needs gateways to connect incompatible communication or embedded systems. It also increases scalability, as several nodes can operate on the same bus line without sacrificing data throughput.
One of the unique aspects of the standard is a physical-layer collision-avoidance ability, which prevents data traffic from jamming or overwhelming nodes.
Each node in the network is assigned an opportunity to transmit. However, if that node has no data to transmit, it hands over priority to the next node, ensuring maximum utilization of speeds and throughput.
It’s also possible to provide power over the 10BASE-T1S network (known as PoDL/Power over Data Lines) as it’s an ac-coupled system, which reduces the amount of cable needed for vehicle networks. It also shrinks connector sizes and increases reliability to the system.
10BASE-T1S Will Drive AE into the Future
The 10BASE-T1S standard will allow automotive Ethernet to expand and evolve along with embedded electronics. This, in turn, will enable vehicle E/E systems to evolve as well with new feature sets, such as multi-drop physical layers, low latencies, and efficient bandwidth utilization.
Automotive suppliers have already started producing 10BASE-T1S components, and new system designs are underway to implement those new devices, as the necessary tools are already available.
10BASE-T1S also allows manufacturers to implement Ethernet-to-the-edge connectivity. One of the key connections in some modern vehicles includes telematics control units (TCUs), an embedded system that handles wireless connectivity to cloud services for any number of applications. The standard optimizes that connectivity; thus, connected nodes can send and receive data in the cloud for everything from tracking to firmware updates.
That said, hurdles must be overcome before the 10BASE-T1S standard is implemented across the entire automotive spectrum, including the notion that the standard will add cost and complexity when designing embedded systems and devices.
Tomi Engdahl says:
What’s the Difference Between CAN and SPE in the Automotive Industry?
Jan. 6, 2023
The CAN bus protocol is being phased out of the automotive industry in favor of single-pair Ethernet due to its increased data bandwidth, node efficiency, security, and more.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21257559/electronic-design-whats-the-difference-between-can-and-spe-in-the-automotive-industry
Tomi Engdahl says:
How 10BASE-T1S Can Drive Wider Adoption of Automotive Ethernet
July 19, 2023
The 10BASE-T1S standard for automotive Ethernet allows manufacturers to implement Ethernet-to-the-edge connectivity and optimize wireless connections to cloud services. However, suppliers must overcome hurdles before adopting it.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21268945/mouser-electronics-how-10baset1s-can-drive-wider-adoption-of-automotive-ethernet?utm_source=EG+ED+Auto+Electronics&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230713179&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
Tomi Engdahl says:
10BASE-T1S PHYs Merge Low-Speed Devices into Automotive Ethernet
Aug. 21, 2023
Basic-connectivity PHY-level interfaces developed by Microchip drive the “Ethernet-ization” of vehicles.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21272105/electronic-design-10baset1s-phys-merge-lowspeed-devices-into-automotive-ethernet?utm_source=EG+ED+Analog+%26+Power+Source&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230817077&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
With all of the multilayered activity associated with a complete network installation along with “ethereal” software to make the network function, there’s still on inescapable fact: Any network’s capabilities begin the physical connection to the media, appropriately known as the PHY layer.
Adding to the automotive Ethernet momentum, Microchip Technology introduced AEC-Q100 Grade 1-qualified 10BASE-T1S Ethernet PHYs designed according to IEEE Std 802.3cg-2019): the LAN8670, LAN8671, and LAN8672. These enable connection of low-speed devices—primarily sensors and actuators—which previously required their own communication systems, into a standard-Ethernet system in automotive applications (Fig. 1).
The 10BASE-T1S device specifications include 10-Mb/s performance, half-duplex mode, flexible topology with multidrop bus line, and point-to-point, all using a single balanced pair of conductors (Fig. 2). The devices also feature enhanced electromagnetic compatibility/electromagnetic interference (EMC/EMI) performance, especially critical in the electrically harsh automotive environment.
Support for time-sensitive networking (TSN)—critical for many applications throughout automotive zonal architectures—enables synchronized timing across far-reaching Ethernet networks
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/15232-10-megabitin-ethernet-tulossa-autoihin
Tomi Engdahl says:
10BASE-T1S PHYs Merge Low-Speed Devices into Automotive Ethernet
Aug. 21, 2023
2
Basic-connectivity PHY-level interfaces developed by Microchip drive the “Ethernet-ization” of vehicles.
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21272105/electronic-design-10baset1s-phys-merge-lowspeed-devices-into-automotive-ethernet?utm_source=EG+ED+Auto+Electronics&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=CPS230824112&o_eid=7211D2691390C9R&rdx.identpull=omeda|7211D2691390C9R&oly_enc_id=7211D2691390C9R
With all of the multilayered activity associated with a complete network installation along with “ethereal” software to make the network function, there’s still on inescapable fact: Any network’s capabilities begin the physical connection to the media, appropriately known as the PHY layer.
Adding to the automotive Ethernet momentum, Microchip Technology introduced AEC-Q100 Grade 1-qualified 10BASE-T1S Ethernet PHYs designed according to IEEE Std 802.3cg-2019): the LAN8670, LAN8671, and LAN8672. These enable connection of low-speed devices—primarily sensors and actuators—which previously required their own communication systems, into a standard-Ethernet system in automotive applications (Fig. 1).
Tomi Engdahl says:
LTC4296-1
5-Port SPoE PSE Controller
https://www.analog.com/en/products/ltc4296-1.html?ADICID=EUBA_EMEA-FIN_P328165_etnfi-300×300-ltc4296-1-BBS-aug23#product-overview
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/15739-windowsin-usb-kiihtyy-ennaetysnopeuteen
Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) kehitettiin aikoinaan autojen kommunikointiratkaisuksi kustannusten, painon ja myös standardoidun Ethernet-kommunikaation vuoksi. Yritykset keksivät nopeasti sen potentiaalin ja edut valmistavassa teollisuudessa.
SPE tarjoaa matalan IP-pohjaisen verkkohierarkian. Verkko mahdollistaa laitteiden ja komponenttien liittämisen IP-osoitteiston avulla verkkoselaimella ja mahdollistaa asetusten muuttamisen ja/tai tietojen korjaamisen.
Single Pair Ethernet -verkon yksipariset kaapelituotteet mahdollistavat merkittävästi nopeamman ja helpomman asennuksen. Se myös pienentää asennusvirheiden mahdollisuutta, verrattuna nelipariseen Ethernet -kaapeliin. SPE:n avulla toimilaitteiden ja antureiden tiedot saadaan välitettyä pilveen, tai yritysten toiminnanohjauksen käyttöön.
SPE on kansainvälisesti standardisoitu teknologia IEEE:n mukaisesti. Kolme pääteknologiaa ovat Gigabit Ethernet 802.3ch käyttötarkoituksena kulkuneuvot aina 15 metrin datan siirtoetäisyyksiin. Gigabit Ethernet, 100 Mbit -Ethernet ja 10 Mbit -Ethernet soveltuvat valmistavaan teollisuuteen, koska kahdella ensin mainitulla päästään 40 metrin etäisyyksiin ja 10 Mbit Ethernet mahdollistaa jopa 1000 metrin etäisyydet. Siirtoetäisyyden pituus on todellinen etu kenttäväyläratkaisuissa.
Käytettävissä on kolme erilaista kaapelia seuraavin johdin poikkipinta-aloin; AWG 26, AWG 22 ja AWG 18. AWG 26 on ohuin kaapeli ja soveltuu gigabitin tai 100 megabitin tiedonsiirtoon aina 40 metrin etäisyyteen saakka.
Vaihtoehtoja kaapeleista löytyy kiinteään asennukseen, liikkuvaan asennukseen tai energiansiirtoketjukäyttöön ja robotiikkaan. Kaikki tämä on kuvattu IEC 611563 standardissa. AWG 18 -poikkipinta-ala mahdollistaa jopa 1000 metrin etäisyyden tiedonsiirron liikkuvassa tai kiinteässä asennuksessa.
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2024/01/16/yhden-parin-ethernetiin-valmiskaapeleita/
Yhden parin Single Pair Ethernet-ratkaisu (SPE) kehitettiin alkuaan autojen kommunikointiratkaisuksi, mutta nyt sitä voidaan hyödyntää valmistavassa teollisuudessa. Saksalainen Lapp tarjoaa siihen niin kaapelit kuin liittimet lisäohjeineen Etherline-valikoimassa.
Yhden parin SPE on kansainvälisesti standardisoitu teknologia IEEE:n mukaisesti. Kolme pääteknologiaa ovat Gigabit Ethernet 802.3ch käyttötarkoituksena kulkuneuvot aina 15 metrin datan siirtoetäisyyksiin.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Ethernet tekee autoista ohjelmistopohjaisia
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/15960-ethernet-tekee-autoista-ohjelmistopohjaisia
Autoja on joskus kutsuttu ”tietokoneiksi pyörillä”, mutta tämä visio edellyttää riittävän nopeaa ja edullista tapaa verkottaa auton eri laitteet. Analog Devices ja BMW aikovat nyt mahdollistaa tällaisen ”softamääritetyn” auton ottamalla pikaisesti käyttöön 10 megabitin Ethernetin ajoneuvoissa.
Tekniikkaa kutsutaan nimellä E²B. Se perustuu ADI:n 10BASE-T1S -väyläteknologiaan. Kyse on standardista, joka mahdollistaa 10 megabitin yhteydet autoissa yhdellä kierretyllä parikaapelilla. BMW sanoo ottavansa uuden tekniikan käyttöön ensimmäisenä.
Vuodesta 2018 lähtien ADI on työskennellyt tiiviissä yhteistyössä BMW Groupin kanssa uudella konseptilla, joka yksinkertaistaa Ethernetin tuomista ajoneuvoihin, siis verkon reunalle. Samaan aikaan IEEE802.3cg-ryhmä määritteli uutta 10 Mbps Ethernet-standardia nimeltä 10BASE-T1S, jossa ADI ja BMW Group muiden yritysten joukossa olivat molemmat aktiivisesti mukana.
Tomi Engdahl says:
ADI and the BMW Group Join Forces to Provide Industry-Leading 10Mb Ethernet for Automotive, Enabling Software-Defined Vehicles
https://www.analog.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2024/3-6-2024-adi-bmw-group-join-forces-provide-industry-leading-10mb-ethernet.html
Analog Devices, Inc. (Nasdaq: ADI) and the BMW Group (Nasdaq: BMWYY) today announced an early adoption of E²B™, ADI’s 10BASE-T1S Ethernet to the Edge bus technology within the automotive industry. Automotive Ethernet connectivity is a key enabler of new, zonal architectures in automotive design and supports automotive megatrends such as software-defined vehicles. The BMW Group will be a leading original equipment manufacturer (OEM) to implement the technology, leveraging ADI’s E²B for their ambient lighting system design in the vehicles of the BMW Group in the future.
Since 2018, ADI has been working closely with the BMW Group on a new concept to simplify bringing Ethernet to the Edge. At the same time, the IEEE802.3cg Group was defining a new 10Mbps Ethernet standard called 10BASE-T1S, with ADI and the BMW Group among other companies both actively involved. Using ADI’s 10BASE-T1S E²B technology to remove microcontrollers and move software from edge nodes to central processing units, the BMW Group enables an all-hardware edge node while reducing software development and qualification tasks.
However, many of today’s lighting solutions are complex to implement, use legacy technologies, and are difficult to scale and update as the number of supported LEDs increases. By leveraging the 10BASE-T1S with E²B technology, OEMs can provide a rich customer experience while also synchronizing lighting with other applications in the vehicle. Fully enabling a software-defined lighting system provides improved flexibility, ease of upgrade, and ease of use.
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.single-pair-ethernet.com/en/artikel/cables-single-pair-ethernet-where-are-we-headed
Cables for Single Pair Ethernet: Where are we headed?
Type A: wires with solid wire for permanent installation.
Type B: wires with stranded conductors for flexible applications or vibrations.
Type C: wires with stranded conductors for high dynamic applications (such as drag chains)
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethernet_over_twisted_pair
Tomi Engdahl says:
Softapohjainen auto saa 80 gigabitin dataverkon
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/16719-softapohjainen-auto-saa-80-gigabitin-dataverkon
NXP julkisti keväällä CoreRide-alustan, jolla voidaan toteuttaa ohjelmistopohjainen ajoneuvo. Nyt yhtiön on tuonut alustalle ensimmäiset verkkokytkimensä. Niiden avulla CoreRide-alustalla data liikkuu 80 gigabitin sekuntinopeudella.
S32J tarjoaa 80 Gbps kaistanleveyden 10 megabitin ja 10 gigabitin porteilla sekä kaksi Arm Cortex-R52 -ydintä vastaamaan uusien ajoneuvoarkkitehtuurien erilaisiin vaatimuksiin. S32J-laitteet täyttävät autoteollisuuden ajoitusvaatimukset TSN-tuen (tim-sensitive netowrking) avulla ja tarjoavat vankan ASIL-D-luokan turvallisuuden.
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/tekniset-artikkelit/17055-tsn-ja-ethernet-ovat-avain-ajoneuvojen-reaaliaikaisiin-vaatimuksiin
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.edn.com/tvs-device-protects-automotive-ethernet/
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.edn.com/diodes-afford-esd-protection-for-automotive-networks/#google_vignette
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.edn.com/will-open-source-software-come-to-sdv-rescue/
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/17243-seuraava-autosi-ajaa-ethernetillae
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/17240-uusin-etndigi-ilmestyi-lue-ilmaiseksi
https://issuu.com/etndigi/docs/etndigi_1-2025?fr=xKAE9_zU1NQ
Tomi Engdahl says:
Gigabitin sarjaväylä aikoo korvata CAN-väylän autoissa
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/17600-gigabitin-sarjavaeylae-aikoo-korvata-can-vaeylaen-autoissa
Analog Devicesin kehittämä GMSL-teknologia avataan teollisuusstandardiksi uuden OpenGMSL-yhdistyksen kautta. Mukana laaja joukko autoteollisuuden ja puolijohdeteollisuuden suuria nimiä.
Autoteollisuus on siirtymässä kohti entistä älykkäämpiä järjestelmiä, kuten autonomista ajoa ja edistyneitä kuljettajaa avustavia järjestelmiä (ADAS). Näiden toteutus vaatii ajoneuvojen sisäverkoilta yhä nopeampaa ja luotettavampaa datansiirtoa. Tähän tarpeeseen vastaa uusi OpenGMSL Association, jonka tavoitteena on tehdä gigabitin sarjaväylästä (GMSL) avoin ja yleinen standardi ajoneuvojen sisäiseen tiedonsiirtoon.
OpenGMSL-standardi perustuu Analog Devicesin (ADI) kehittämään Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link -teknologiaan, joka on ollut markkinoilla jo pitkään ja osoittautunut erittäin luotettavaksi. Teknologiaa on toimitettu yli miljardiin piiriin, ja se on jo käytössä yli 25 autonvalmistajalla sekä 50 Tier-1-toimittajalla. Nyt tämä teknologia aiotaan avata koko teollisuuden käyttöön avoimen standardin muodossa. Tavoitteena on luoda yhteinen tekninen perusta, jonka avulla eri valmistajien järjestelmät ja komponentit voivat toimia saumattomasti yhteen.
OpenGMSL-standardin avulla halutaan parantaa laitteiden yhteentoimivuutta eri valmistajien välillä. Tämä tarkoittaa, että autovalmistajat ja toimittajat voivat käyttää toistensa komponentteja ilman, että yhteensopivuudesta tarvitsee erikseen huolehtia.
OpenGMSL-teknologian käyttökohteet ovat laajat. Ensinnäkin standardi on suunniteltu tukemaan autonomista ajamista, jossa ajoneuvon tarvitsee siirtää suuria määriä dataa reaaliaikaisesti kameroilta ja antureilta laskentayksiköille. Toiseksi teknologia sopii edistyneisiin kuljettajaa avustaviin järjestelmiin eli ADAS-järjestelmiin, jotka hyödyntävät videokuvaa ja anturidataa tehdäkseen nopeita päätöksiä liikenteessä. Kolmanneksi GMSL sopii infotainment-järjestelmiin, joissa tarvitaan korkeaa kaistanleveyttä, matalaa viivettä ja luotettavaa yhteyttä useiden näyttöjen, kameroiden ja äänentoistojärjestelmien välillä.
OpenGMSL Associationin perustajajäseniin kuuluu merkittävä määrä alan johtavia yrityksiä, jotka edustavat autoteollisuuden, puolijohdeteollisuuden ja testauslaitteistojen valmistuksen huippua. Analog Devices toimii teknologian alkuperäisenä kehittäjänä ja aloitteen veturina. Qualcomm Technologies tuo mukaan osaamisensa tehokkaiden, ajoneuvoihin soveltuvien piirisarjojen kehittämisessä. Hyundai Mobis on merkittävä toimija autoelektroniikan ja ajoneuvojärjestelmien toimittajana, ja DENSO Corporation on yksi maailman suurimmista Tier-1-toimittajista. Aptiv tunnetaan ajoneuvoteknologian edelläkävijänä, erityisesti ohjelmistojen ja sähköjärjestelmien saralla. GlobalFoundries tarjoaa puolestaan edistyneet valmistusalustat puolijohteille, joita tarvitaan nopeaan ja energiatehokkaaseen tiedonsiirtoon.
OpenGMSL Association toimii voittoa tavoittelemattomana yhdistyksenä, jolla on itsenäinen hallitus.