http://vitorr.com/post-details.php?postid=2615
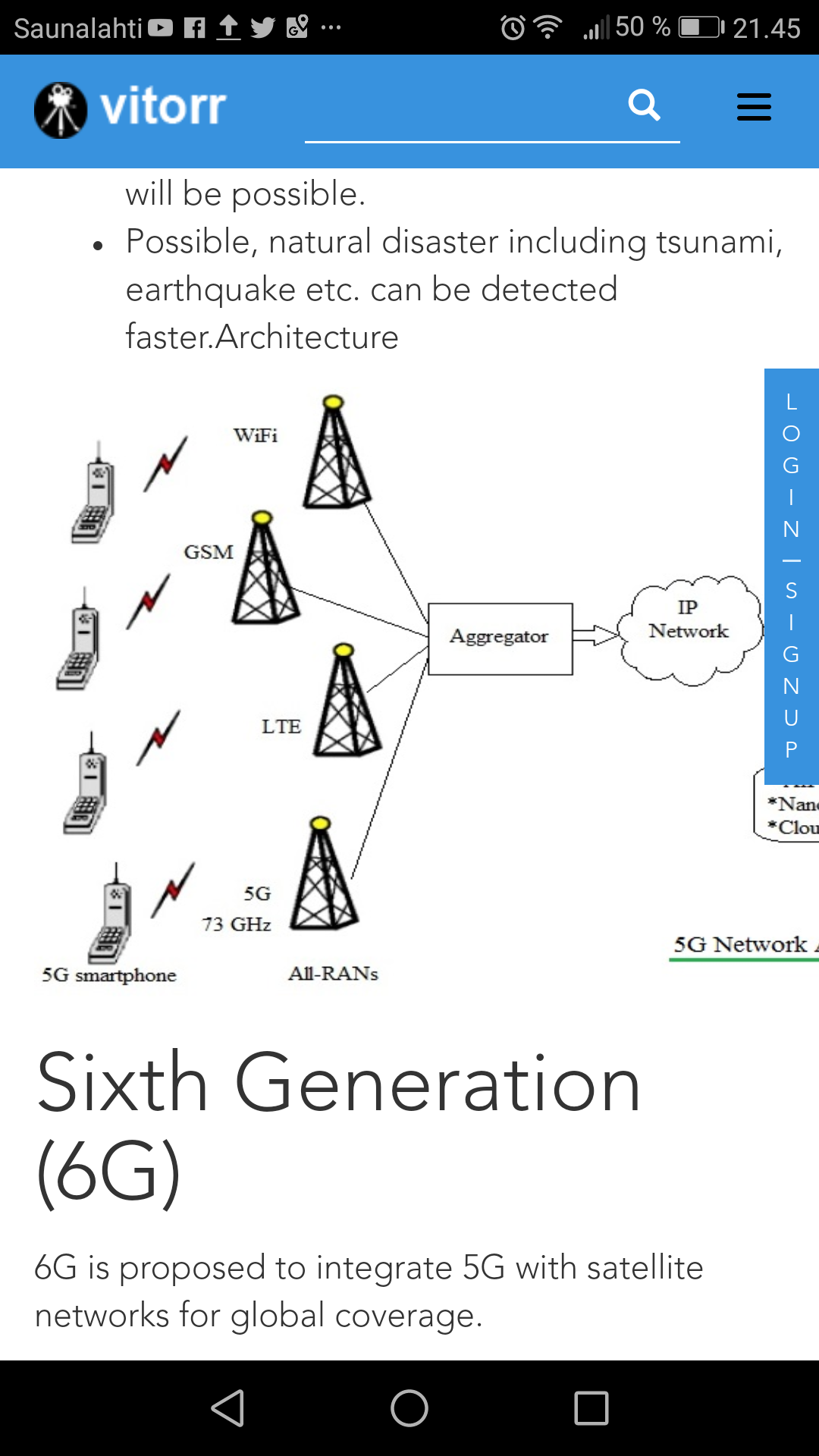
The cellular wireless Generation (G) generally refers to a change in the nature of the system, speed, technology and frequency. Each generation have some standards, capacities, techniques and new features which differentiate it from the previous one.
Now 5G is hot technology at the top of the hype cycle. But that’s not the end of story, because when we will see that 5G does not fullfill all the promises, we start looking for to implement next version after it: 6G.
458 Comments
Tomi Engdahl says:
Kaikkein nopeimpien langattomien signaalien testaaminen onnistuu nyt tabletilla
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/17636-kaikkein-nopeimpien-langattomien-signaalien-testaaminen-onnistuu-nyt-tabletilla
Saksalainen Aaronia esittelee San Franciscon IMS 2025 -messuilla maailman nopeimmat kannettavat reaaliaikaiset spektrianalysaattorit, jotka mahdollistavat jopa yli 3 000 GHz/s pyyhkäisyn – ja kaiken tämän voi tehdä kentällä suoraan tabletilla.
Uusi SPECTRAN V6 MOBILE on maailman ensimmäinen reaaliaikainen spektrianalysaattori, jossa yhdistyvät 490 MHz reaaliaikainen kaistanleveys, 9 kHz – 140 GHz taajuusalue ja kenttäkäyttöön suunniteltu tablettimuotoilu. Laitteisto on varustettu AMD Ryzen 7949 HF -prosessorilla ja 64 Gt LPDDR5x-muistilla, ja siihen mahtuu jopa 16 Tt SSD-tallennustilaa. Käyttöaikaa varmistavat kaksi kuumana vaihdettavaa akkua.
Uutuus mahdollistaa esimerkiksi uusien IEEE 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6E/7) -verkkojen 320 MHz kanavien täyden reaaliaikaisen tallennuksen sekä millimetriaaltotutkien (mmWave) testauksen – myös auto- ja ilmailuteollisuuden tarpeisiin.
Samassa yhteydessä Aaronia lanseeraa SPECTRAN V6 XPR -sarjan USB-liitäntäiset spektrianalysaattorit, joissa yhdistyvät yli 3 THz/s pyyhkäisynopeus ja kehittynyt waveguide-tekniikka. Erityisesti malli V6 PLUS XPR 250XB-WR12 on suunniteltu 76–81 GHz tutkasignaalien tarkkaan analysointiin – esimerkiksi itseajavien ajoneuvojen tutkajärjestelmissä.
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://etn.fi/index.php/13-news/17650-uusi-gan-transistori-voi-mullistaa-6g-verkkojen-radiotaajuuspiirit
Tomi Engdahl says:
Researchers claim the new 6G system can jam US F-35 stealth fighter jet radars. https://bit.ly/4jRqa3R
Tomi Engdahl says:
Kansallinen 6G-verkkojen tiekartta tulossa
https://www.uusiteknologia.fi/2025/06/18/kansallinen-6g-verkkojen-tiekartta-tulossa/
iikenne- ja viestintäministeriö tietoliikenteen uuden työryhmän valmisteleman kansallisen 6G-tiekartan toteuttamista. Tulossa on suunnitelma, jossa esitetään tärkeimmät askelmerkit 2030-luvulla tulevaan seuraavan sukupolven matkaviestinteknologioiden kehittämiseen ja käyttöönottoon.
Tulevassa Suomen 6G-tiekartassa on nimetty neljä painopistettä tavoitteiden saavuttamiseksi ja jokaiselle painopisteelle on tunnistettu keskeisimmät askelmerkit vuosille 2025–2030. EU:ssa ja kansainvälisillä foorumeilla vaikuttaminen korostuvat kaikissa painopisteissä.
’’Tiekartan avulla varmistamme, että pysymme kehityksen kärjessä ja luomme edellytyksiä kasvulle, sanoo liikenne- ja viestintäministeri Lulu Ranne. Suomi julkaiseen hänen mukaansa 6G-tiekartan ensimmäisten maiden joukossa. Tiekartan painopisteet ovat sääntely- ja taajuustyö, jossa kansainvälisten päätösten ja kansallisen taajuuksien saatavuuden tulee tukea sekä teknologian kehitystä että investointien suunnittelua.
6G:n käyttöönotto edellyttää oikein ajoitettuja linjauksia tulevista verkkotoimilupaehdoista. Taajuuksien toimiva jakaminen edellyttää tutkimuksia sekä uusia sääntely-, teknologia- ja standardointiratkaisuja. 6G:ssä turvallisuusvaatimusten tulee olla myös standardeihin sisäänrakennettuja suunnitteluvaiheesta lähtien (ns. secure-by-design-periaate). 6G:n strategisiin turvallisuusriskeihin vastataan ajantasaisella ja teknologisen kehityksen huomioivalla sääntelyllä. Riskienhallinnan tulisi olla ennakoivaa, jotta siihen liittyvät toimet eivät hidasta 6G:n käyttöönottoa.
Tomi Engdahl says:
Eurobites: 6G must learn from ‘mistakes of 5G,’ telcos tell 3GPP
Also in today’s EMEA regional roundup: Vodafone and friends test 1024 QAM; cablecos sign agreement on AAE-2 subsea link; telcos can’t get enough of GenAI.
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/eurobites-6g-must-learn-from-mistakes-of-5g-telcos-tell-3gpp
The Next Generation Mobile Networks Alliance (NGMN), which counts BT, Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone and Orange among its list of members, has issued a joint statement to standards-setting body 3GPP telling it that 6G can’t be just “another generational shift” and that lessons must be learned from “the mistakes of 5G.” The introduction of 6G should also not, they insist, cost operators more than it needs to: “The introduction of 6G should not necessitate a forced hardware refresh,” says the statement. “While new radio equipment is required for deployment in new frequency bands, the evolution toward 6G in existing bands should primarily occur through software upgrades, ensuring a smooth transition.” (See 6G apathy outside China is rife and Sensing a new 6G use case.)
Tomi Engdahl says:
Vodafone and friends test 1024 QAM for faster download
Vodafone, Nokia, Qualcomm and Xiaomi have been carrying out more tests of a technique called 1024 quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) to increase data throughput on 5G transmission, claiming a data boost of almost 25% this time around. The currently used transmission system is based on 256 QAM. Boffins from the quartet of companies achieved download speeds of 1.7 Gbit/s on 3.5GHz spectrum using a Xiaomi 15 Ultra smartphone equipped with the Snapdragon 8 Elite Mobile Platform and Nokia’s Habrok 64 massive MIMO radios. The 1024 QAM technique will, it is claimed, help save energy by increasing data throughput without the need for additional hardware at the mobile basestation.
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/eurobites-6g-must-learn-from-mistakes-of-5g-telcos-tell-3gpp
Tomi Engdahl says:
Ericsson and Samsung clash over open RAN in 6G
Reintegrating central and distributed unit functions in a single box makes economic and technical sense in 6G, according to Ericsson. But Samsung disagrees.
https://www.lightreading.com/open-ran/ericsson-and-samsung-clash-over-open-ran-in-6g
Tomi Engdahl says:
Eurobites: Ericsson claims network-autonomy breakthrough with TDC Net
Also in today’s EMEA regional roundup: APIs venture attracts more big names; BBC threatens legal action against Perplexity; UK heatwave has chilling effect on broadband speeds.
https://www.lightreading.com/network-automation/eurobites-ericsson-claims-network-autonomy-breakthrough-with-tdc-net